Chat-based assistants powered by Retrieval Augmented Technology (RAG) are remodeling buyer assist, inner assist desks, and enterprise search, by delivering quick, correct solutions grounded in your individual knowledge. With RAG, you need to use a ready-to-deploy basis mannequin (FM) and enrich it with your individual knowledge, making responses related and context-aware with out the necessity for fine-tuning or retraining. Working these chat-based assistants on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) offers you the flexibleness to make use of quite a lot of FMs, retaining full management over your knowledge and infrastructure.
Amazon EKS scales along with your workload and is cost-efficient for each regular and fluctuating demand. As a result of EKS is licensed Kubernetes-conformant, it’s appropriate with current functions operating on an ordinary Kubernetes setting, whether or not hosted on on-premises knowledge facilities or public clouds. To your knowledge airplane, you’ll be able to benefit from a variety of compute choices, together with CPUs, GPUs, AWS purpose-built AI chips (AWS Inferentia and AWS Trainium) and ARM-based CPU architectures (AWS Graviton), to match efficiency and value necessities. Such flexibility makes Amazon EKS a great candidate for operating heterogeneous workloads as a result of you’ll be able to compose totally different compute substrates, inside the identical cluster, to optimize each efficiency and value effectivity.
NVIDIA NIM microservices include microservices that deploy and serve FMs, integrating with AWS providers similar to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2), Amazon EKS, and Amazon SageMaker. NIM microservices are distributed as Docker containers and can be found by the NVIDIA NGC Catalog. Deploying GPU-accelerated fashions manually requires you to pick and configure runtimes similar to PyTorch or TensorFlow, arrange inference servers similar to Triton, implement mannequin optimizations, and troubleshoot compatibility points. This takes engineering time and experience. NIM microservices remove this complexity by automating these technical choices and configurations for you.
The NVIDIA NIM Operator is a Kubernetes administration software that facilitates the operation of model-serving elements and providers. It handles giant language fashions (LLMs), embedders, and different mannequin sorts by NVIDIA NIM microservices inside Kubernetes environments. The Operator streamlines microservice administration by three major {custom} assets. First, the NIMCache useful resource facilitates mannequin downloading from NGC and community storage persistence. This permits a number of microservice situations to share a single cached mannequin, enhancing microservice startup time. Second, the NIMService useful resource manages particular person NIM microservices, creating Kubernetes deployments inside specified namespaces. Third, the NIMPipeline useful resource features as an orchestrator for a number of NIM service assets, permitting coordinated administration of service teams. This structure permits environment friendly operation and lifecycle administration, with specific emphasis on decreasing inference latency by mannequin caching and supporting automated scaling capabilities.
NVIDIA NIM, coupled with the NVIDIA NIM Operator, present a streamlined resolution to handle the deployment complexities said within the opening. On this put up, we display the implementation of a sensible RAG chat-based assistant utilizing a complete stack of recent applied sciences. The answer makes use of NVIDIA NIMs for each LLM inference and textual content embedding providers, with the NIM Operator dealing with their deployment and administration. The structure incorporates Amazon OpenSearch Serverless to retailer and question high-dimensional vector embeddings for similarity search.
The underlying Kubernetes infrastructure of the answer is supplied by EKS Auto Mode, which helps GPU-accelerated Amazon Machine Photos (AMIs) out of the field. These pictures embrace the NVIDIA system plugin, the NVIDIA container toolkit, precompiled NVIDIA kernel drivers, the Bottlerocket working system, and Elastic Material Adapter (EFA) networking. You should use Auto Mode with Accelerated AMIs to spin up GPU situations, with out manually putting in and configuring GPU software program elements. Merely specify GPU-based occasion sorts when creating Karpenter NodePools, and EKS Auto Mode will launch GPU-ready employee nodes to run your accelerated workloads.
Answer overview
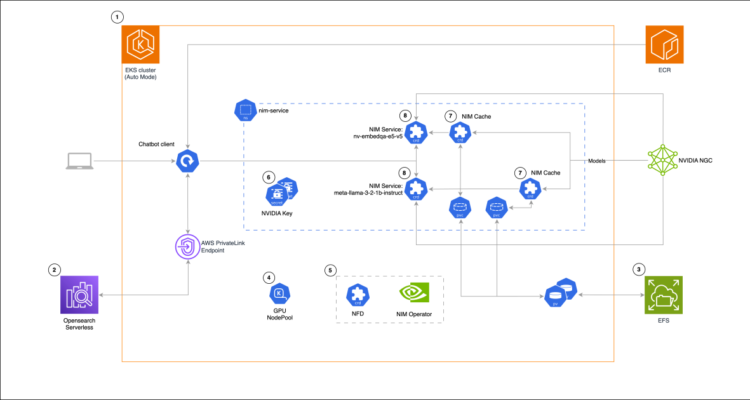
The next structure diagram exhibits how NVIDIA NIM microservices operating on Amazon EKS Auto Mode energy our RAG chat-based assistant resolution. The design, proven within the following diagram, combines GPU-accelerated mannequin serving with vector search in Amazon OpenSearch Serverless, utilizing the NIM Operator to handle mannequin deployment and caching by persistent Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) storage.

Answer diagram (numbers point out steps within the resolution walkthrough part)
The answer follows these high-level steps:
- Create an EKS cluster
- Arrange Amazon OpenSearch Serverless
- Create an EFS file system and arrange vital permissions
- Create Karpenter GPU
NodePool - Set up NVIDIA Node Function Discovery (NFD) and NIM Operator
- Create nim-service namespace and NVIDIA secrets and techniques
- Create
NIMCaches - Create
NIMServices
Answer walkthrough
On this part, we stroll by the implementation of this RAG chat-based assistant resolution step-by-step. We create an EKS cluster, configure Amazon OpenSearch Serverless and EFS storage, arrange GPU-enabled nodes with Karpenter, deploy NVIDIA elements for mannequin serving, and eventually combine a chat-based assistant consumer utilizing Gradio and LangChain. This end-to-end setup demonstrates how you can mix LLM inference on Kubernetes with vector search capabilities, forming the inspiration for a scalable, production-grade system—pending the addition of monitoring, auto scaling, and reliability options.
Conditions
To start, guarantee you’ve put in and arrange the next required instruments:
- AWS CLI (model aws-cli/2.27.11 or later)
kubectleksctl(use model v0.195.0 or later to assist Auto Mode)- Helm
These instruments must be correctly configured based on the Amazon EKS setup documentation.
Clone the reference repository and cd into the foundation folder:
Atmosphere setup
You want an NGC API key to authenticate and obtain NIM fashions. To generate the important thing, you’ll be able to enroll (free of charge) within the NVIDIA Developer Program after which comply with the NVIDIA tips.
Subsequent, arrange just a few setting variables (change the values along with your info):
Sample deployment
To carry out the answer, full the steps within the following sections.
Create an EKS cluster
Deploy the EKS cluster utilizing EKS Auto Mode, with eksctl :
Pod Identification Associations join Kubernetes service accounts to AWS Identification and Entry Administration (IAM) roles, permitting pods to entry AWS providers securely. On this configuration, a service account shall be created and related to an IAM position, granting it full permissions to OpenSearch Serverless (in a manufacturing setting, prohibit privileges based on the precept of least privilege).
NIMCaches require quantity AccessMode: ReadWriteMany. Amazon Elastic Block Retailer (Amazon EBS) volumes supplied by EKS Auto Mode aren’t appropriate as a result of they assist ReadWriteOnce solely and might’t be mounted by a number of nodes. Storage choices that assist AccessMode: ReadWriteMany embrace Amazon EFS, as proven on this instance, or Amazon FSx for Lustre, which affords greater efficiency for workloads with better throughput or latency necessities.
The previous command will take a couple of minutes to be accomplished. When it’s accomplished, eksctl configures your kubeconfig and factors it to the brand new cluster. You possibly can validate that the cluster is up and operating and that the EFS addon is put in by getting into the next command:
Anticipated output:
Arrange Amazon OpenSearch Serverless
A vector database shops and searches by numerical representations of textual content (embeddings). Such a part is important in RAG chat-based assistant architectures as a result of it facilitates discovering related info associated to a consumer query based mostly on semantic similarity moderately than precise key phrase matches.
We use Amazon OpenSearch Service because the vector database. OpenSearch Service offers a managed resolution for deploying, working, and scaling OpenSearch clusters inside AWS Cloud infrastructure. As a part of this service, Amazon OpenSearch Serverless affords an on-demand configuration that mechanically handles scaling to match your utility’s necessities.
First, utilizing AWS PrivateLink, create a personal connection between the cluster’s Amazon Digital Personal Cloud (Amazon VPC) connection and Amazon OpenSearch Serverless. This retains visitors inside the AWS community and avoids public web routing.
Enter the next instructions to retrieve the cluster’s digital non-public cloud (VPC) ID, CIDR block vary, and subnet IDs, and retailer them in corresponding setting variables:
Use the next code to create a safety group for OpenSearch Serverless within the VPC, add an inbound rule to the safety group permitting HTTPS visitors (port 443) out of your VPC’s CIDR vary, and create an OpenSearch Serverless VPC endpoint related to the subnets and safety group:
Within the following steps, create an OpenSearch Serverless assortment (a logical unit to retailer and set up paperwork).
- Create an encryption coverage for the gathering:
- The community coverage that restricts entry to the gathering to solely come by a selected VPC endpoint:
- The information coverage that grants permissions to the IAM chat-based assistant position for interacting with indices within the assortment:
- The OpenSearch assortment itself:
Create EFS file system and arrange vital permissions
Create an EFS file system:
EFS requires mount targets, that are VPC community endpoints that join your EKS nodes to the EFS file system. These mount targets should be reachable out of your EKS employee nodes, and entry is managed utilizing safety teams.
- Execute the next command to arrange the mount targets and configure the required safety group guidelines:
- Create the
StorageClassin Amazon EKS for Amazon EFS:
- Validate the EFS storage class:
These are the anticipated outcomes:
Create Karpenter GPU NodePool
To create the Karpenter GPU NodePool, enter the next code:
This NodePool is designed for GPU workloads utilizing AWS G5 situations, which function NVIDIA A10G GPUs. The taint ensures that solely workloads particularly designed for GPU utilization shall be scheduled on these nodes, sustaining environment friendly useful resource utilization. In a manufacturing setting, you would possibly wish to think about using Amazon EC2 Spot Situations as nicely to optimize on prices.
Enter the command to validate profitable creation of the NodePool:
These are the anticipated outcomes:
gpu-node-pool was created and has 0 nodes. To examine nodes additional, enter this command:
That is the anticipated output:
There are two situations, launched by EKS Auto Mode with non-accelerated Bottlerocket Amazon Machine Picture (AMI) variant aws-k8s-1.32, and CPU-only (non-GPU) occasion kind c6g.
Set up NVIDIA NFD and NIM Operator
The NFD is a Kubernetes plugin that identifies obtainable {hardware} capabilities and system settings. NFD and NIM Operator are put in utilizing Helm charts, every with their very own {custom} useful resource definitions (CRDs).
- Earlier than continuing with set up, confirm if associated CRDs exist in your cluster:
If these CRDs aren’t current, each instructions will return no outcomes.
- Add Helm repos:
- Set up the NFD dependency for NIM Operator:
- Validate the pods are up and CRDs have been created:
Anticipated output:
Anticipated output:
- Set up the NIM Operator:
You would possibly want to make use of model v1.0.1 for the NIM Operator as a substitute of v2.0.0 as proven within the previous code instance as a result of often you would possibly obtain a “402 Fee Required” message.
- Validate the pod is up and CRDs have been created:
Anticipated output:
Anticipated output:
Create nim-service namespace and NVIDIA secrets and techniques
On this part, create the nim-service namespace and add two secrets and techniques containing your NGC API key.
- Create namespace and secrets and techniques:
- Validate secrets and techniques have been created:
The next is the anticipated consequence:
ngc-secret is a Docker registry secret used to authenticate and pull NIM container pictures from NVIDIA’s NGC container registry.
ngc-api-secret is a generic secret utilized by the mannequin puller init container to authenticate and obtain fashions from the identical registry.
Create NIMCaches
RAG enhances chat functions by enabling AI fashions to entry both inner domain-specific data or exterior data bases, decreasing hallucinations and offering extra correct, up-to-date responses. In a RAG system, a data base is created from domain-specific paperwork. These paperwork are sliced into smaller items of textual content. The textual content items and their generated embeddings are then uploaded to a vector database. Embeddings are numerical representations (vectors) that seize the which means of textual content, the place comparable textual content content material leads to comparable vector values. When questions are obtained from customers, they’re additionally despatched with their respective embeddings to the database for semantic similarity search. The database returns the closest matching chunks of textual content, that are utilized by an LLM to offer a domain-specific reply.
We use Meta’s llama-3-2-1b-instruct as LLM and NVIDIA Retrieval QA E5 (embedqa-e5-v5) as embedder.
This part covers the deployment of NIMCaches for storing each the LLM and embedder fashions. Native storage of those fashions accelerates pod initialization by eliminating the necessity for repeated downloads. Our llama-3-2-1b-instruct LLM, with 1B parameters, is a comparatively small mannequin and makes use of 2.5 GB of cupboard space. The storage necessities and initialization time improve when bigger fashions are used. Though the preliminary setup of the LLM and embedder caches takes 10–quarter-hour, subsequent pod launches shall be sooner as a result of the fashions are already obtainable within the cluster’s native storage.
Enter the next command:
That is the anticipated output:
NIMCaches will create PersistentVolumes (PVs) and PersistentVolumeClaims (PVCs) to retailer the fashions, with STORAGECLASS efs:
The next is the anticipated output:
Enter the next to validate NIMCaches:
That is the anticipated output (STATUS will keep initially clean, then develop into InProgress for 10–15 minutes till mannequin obtain is full):
Create NIMServices
NIMServices are {custom} assets to handle NVIDIA NIM microservices. To deploy the LLM and embedder providers enter the next:
The next is the anticipated output:
Validate the NIMServices:
The next is the anticipated output:
Our fashions are saved in an EFS quantity, which is mounted to the EC2 situations as a PVC. That interprets to sooner pod startup instances. In reality, discover within the previous instance that the NIMServices are prepared in roughly 5 minutes. This time consists of GPU node(s) launch from Karpenter and container picture pull and launch.
In comparison with the ten–quarter-hour required for internet-based mannequin downloads, as skilled throughout the NIMCaches deployment, loading fashions from the native cache reduces startup time significantly, enhancing the general system scaling velocity. Must you want much more performing storage options, you could possibly discover options similar to Amazon FSx for Lustre.
Enter the next command to verify the nodes once more:
The next is the anticipated output:
Karpenter launched two new GPU situations to assist NIMServices, with a Bottlerocket accelerated AMI variant Bottlerocket (EKS Auto, Nvidia) 2025.4.21 (aws-k8s-1.32-nvidia). The quantity and kind of situations launched would possibly range relying on Karpenter’s algorithm, which takes into consideration parameters similar to occasion availability and value.
Verify that the NIMService STATUS is Prepared earlier than progressing additional.
Chat-based assistant consumer
We now use a Python consumer, implementing the chat-based assistant interface, utilizing the Gradio and LangChain libraries. Gradio creates the net interface and chat elements, dealing with the frontend presentation. LangChain connects varied elements and implements RAG by a number of providers in our EKS cluster. Meta’s llama-3-2-1b-instruct serves as the bottom language mannequin, and nv-embedqa-e5-v5 creates textual content embeddings. OpenSearch acts because the vector retailer, managing these embeddings and enabling similarity search. This setup permits the chat-based assistant to retrieve related info and generate contextual responses.

Sequence diagram displaying question-answering workflow with doc add course of
- Enter the next instructions to deploy the consumer, hosted on Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) as a container picture within the public gallery (the appliance’s supply recordsdata can be found within the
consumerfolder of the cloned repository):
- Test the consumer pod standing:
The next is the instance output:
- Port-forward the consumer’s service:
- Open a browser window at
http://127.0.0.1:7860.
Within the following screenshot, we prompted the chat-based assistant a few subject that isn’t in its data base but: “What’s Amazon Nova Canvas.”

The chat-based assistant can’t discover info on the subject and might’t formulate a correct reply.
- Obtain the file at location:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/pdfs/ai/responsible-ai/nova-canvas/nova-canvas.pdfand add its embeddings to OpenSearch Serverless utilizing the consumer UI, switching to the Doc add tab, within the prime left, as proven within the following screenshot.

The anticipated result’s nova-canvas.pdf showing the listing of uploaded recordsdata, as proven within the following screenshot.

- Wait 15–30 seconds for OpenSearch Serverless to course of and index the info. Ask the identical query, “What’s Amazon Nova Canvas,” and you’ll obtain a distinct reply, as proven within the following screenshot.

Cleanup
To scrub up the cluster and the EFS assets created to date, enter the next command:
Wait roughly 30 seconds for the mount targets to be eliminated, then enter the next command:
To delete the OpenSearch Serverless assortment and insurance policies, enter the next command:
Conclusion
On this put up, we confirmed how you can deploy a RAG-enabled chat-based assistant on Amazon EKS, utilizing NVIDIA NIM microservices, integrating an LLM for textual content technology, an embedding mannequin, and Amazon OpenSearch Serverless for vector storage. Utilizing EKS Auto Mode with GPU-accelerated AMIs, we streamlined our deployment by automating the setup of GPU infrastructure. We specified GPU-based occasion sorts in our Karpenter NodePools, and the system mechanically provisioned employee nodes with all vital NVIDIA elements, together with system plugins, container toolkit, and kernel drivers. The implementation demonstrated the effectiveness of RAG, with the chat-based assistant offering knowledgeable responses when accessing related info from its data base. This structure showcases how Amazon EKS can streamline the deployment of AI options, sustaining production-grade reliability and scalability.
As a problem, strive enhancing the chat-based assistant utility by implementing chat historical past performance to protect context throughout conversations. This enables the LLM to reference earlier exchanges and supply extra contextually related responses. To additional learn to run synthetic intelligence and machine studying (AI/ML) workloads on Amazon EKS, try our EKS finest practices information for operating AI/ML workloads, be a part of certainly one of our Get Fingers On with Amazon EKS occasion sequence, and go to AI on EKS deployment-ready blueprints.
Concerning the authors
 Riccardo Freschi is a Senior Options Architect at AWS who focuses on Modernization. He helps companions and prospects remodel their IT landscapes by designing and implementing trendy cloud-native architectures on AWS. His focus areas embrace container-based functions on Kubernetes, cloud-native growth, and establishing modernization methods that drive enterprise worth.
Riccardo Freschi is a Senior Options Architect at AWS who focuses on Modernization. He helps companions and prospects remodel their IT landscapes by designing and implementing trendy cloud-native architectures on AWS. His focus areas embrace container-based functions on Kubernetes, cloud-native growth, and establishing modernization methods that drive enterprise worth.
 Christina Andonov is a Sr. Specialist Options Architect at AWS, serving to prospects run AI workloads on Amazon EKS with open supply instruments. She’s captivated with Kubernetes and identified for making advanced ideas simple to know.
Christina Andonov is a Sr. Specialist Options Architect at AWS, serving to prospects run AI workloads on Amazon EKS with open supply instruments. She’s captivated with Kubernetes and identified for making advanced ideas simple to know.