We’re excited to announce the final availability of GPU partitioning with Amazon SageMaker HyperPod, utilizing NVIDIA Multi-Occasion GPU (MIG). With this functionality you may run a number of duties concurrently on a single GPU, minimizing wasted compute and reminiscence assets that outcome from dedicating complete {hardware} (for instance, complete GPUs) to duties that may under-utilize the assets. By permitting extra customers and duties to entry GPU assets concurrently, you may scale back growth and deployment cycle instances whereas supporting a various mixture of workloads operating in parallel on a single bodily GPU, all with out ready for full GPU availability.
Information scientists run a number of light-weight duties on reserved accelerated compute assets and must drive environment friendly utilization for inference (for instance, serving a language mannequin), analysis (for instance, mannequin prototyping), and interactive duties (for instance, Jupyter notebooks for picture classification experimentation). These duties sometimes don’t require complete GPUs to run effectively, not to mention 8 GPUs. Cluster directors need to allow cluster personas—knowledge scientists, ML engineers, infrastructure groups—to run extra workloads concurrently on the identical GPUs, whereas preserving efficiency assurances and workload isolation boundaries, maximizing cluster-wide utilization, and sustaining full visibility into GPU compute and reminiscence utilization.
On this put up, we dive deep into methods to arrange and use MIG on SageMaker HyperPod, exhibit sensible examples for each inference and interactive workloads, and share greatest practices for maximizing the worth of this new functionality.
MIG in Amazon SageMaker HyperPod
In 2020, NVIDIA launched NVIDIA Multi-Occasion GPU (MIG), alongside the Ampere structure that powers the NVIDIA A100 (for instance: Amazon EC2 P4 – SageMaker ml.p4d.24xlarge cases) and NVIDIA A10G (Amazon EC2 G5) GPUs (be aware: G5 cases don’t assist MIG). With MIG, directors can partition a single GPU into a number of smaller GPU models (known as “MIG gadgets”). Every MIG partition operates as an impartial, fully-isolated GPU occasion with its personal reminiscence partition, cache, and compute cores. This isolation permits predictable efficiency and helps stop useful resource conflicts between duties.
With MIG assist on Amazon SageMaker HyperPod, directors can now maximize GPU utilization via versatile useful resource partitioning. This functionality addresses key challenges with GPU useful resource administration:
- Simplified arrange administration: Take away the complexity of scaling GPU partitions with simple-to-use setup throughout SageMaker HyperPod capabilities.
- Useful resource optimization: Partition highly effective GPUs into right-sized partitions for smaller workloads, equivalent to analysis experiments or small language mannequin inference.
- Workload isolation: Run a number of impartial duties concurrently with predictable efficiency, enabling a number of workforce members to work independently on the identical GPU {hardware} whereas sustaining efficiency assurances and workload isolation.
- Price effectivity: Maximize the worth of GPU infrastructure by operating a number of workloads concurrently as a substitute of dedicating complete GPUs to smaller duties.
- Observability: Monitor real-time efficiency metrics and useful resource utilization, optimizing process effectivity throughout GPU partitions.
- Quota administration: Allocate fine-grained compute quota throughout groups, optimizing compute useful resource distribution.
“We’ve been utilizing SageMaker HyperPod for over a yr now, for a mixture of inference and coaching. Partitioning GPUs with MIG know-how for inference has allowed us to considerably enhance the effectivity of our cluster, by maximizing the variety of duties we will run in parallel. It’s actually helped us unlock the complete potential of SageMaker HyperPod.”
– Arthur Hussey, Technical employees at Orbital Supplies, a United Kingdom-based startup, who develops and runs AI fashions that may generate and simulate novel supplies at scale.
MIG is helpful while you need to allocate your higher-powered cases to be used by a number of customers or duties of their respective remoted environments. For instance, totally different groups inside a company can run their fashions concurrently on the identical bodily GPU, every with their very own devoted assets. This strategy improves general GPU utilization and effectivity, making it a cheap answer for organizations trying to maximize their GPU infrastructure funding. Some extra key use instances embody:
- Useful resource-guided mannequin serving: Organizations deploying a number of mannequin variations (totally different sizes, quantization ranges) can match every mannequin to an appropriately sized MIG occasion. A quantized 10B parameter mannequin may run effectively on a GPU partition, whereas a full-precision mannequin wants a bigger partition—each served from the identical bodily GPU with QoS assurances. One other instance, as demonstrated under is the totally different {hardware} necessities even inside a single inference cycle—the prefill part requires extra compute for the GEMMs for KV Cache calculations, whereas the decode part could require extra GPU reminiscence (and reminiscence bandwidth).
- Blended workloads: Information science groups usually must run Jupyter notebooks for experimentation, batch inference pipelines, and occasional fine-tuning concurrently. MIG permits these various workloads—every with totally different useful resource necessities—to coexist on the identical GPU with out interference.
- Improvement and testing effectivity: CI/CD pipelines for ML fashions require remoted testing environments. MIG lets groups spin up a number of GPU cases for parallel mannequin validation, smoke assessments, and A/B testing frameworks with out provisioning separate bodily {hardware} for every take a look at suite. This will increase the iteration instances for every deployment.
Structure
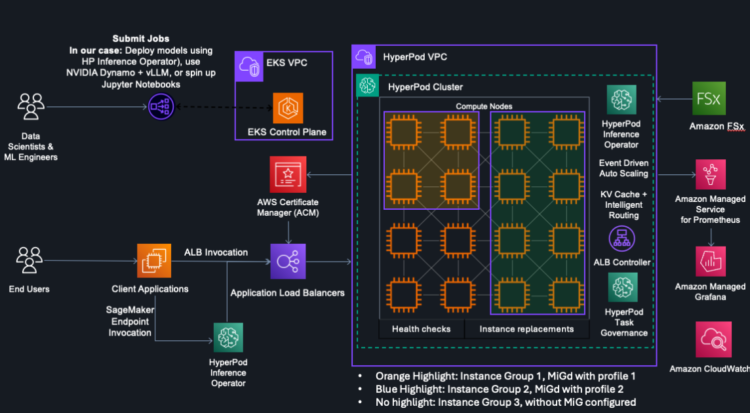
Within the following instance structure MIG is deployed on a SageMaker HyperPod EKS cluster of 16 ml.p5en.48xlarge cases. The cluster consists of three occasion teams, every configured with totally different profiles. The cluster additionally makes use of the HyperPod Inference Operator to deploy fashions. MIG notably shines in inference situations, offering predictable latency, flexibility in deployment, useful resource optimization and maximal GPU utilization, High quality of Service (QoS) assurances, and price effectivity.

Deep dive: What’s NVIDIA Multi-Occasion GPU (MIG)?
Launched by NVIDIA with the Ampere structure, and refined in Hopper and Blackwell generations, MIG creates remoted partitions with devoted streaming multiprocessors (SM), L2 cache slices, reminiscence controllers, and DRAM tackle buses. A single GPU “occasion” consists of GPU slices (smallest fraction of a GPU that mixes a single GPU reminiscence slice and a single GPU SM slice), and GPU engines (DMAs, NVDECs). To study extra in regards to the terminology of what’s included inside every GPU occasion, take a look at MIG ideas.
Every GPU is partitioned utilizing reminiscence slices, thus offering a sensible answer for dividing GPU assets successfully. MIG helps the partition of a single GPU into a number of separate cases, every with its personal devoted assets. That is notably helpful for workloads that don’t require the complete energy of a contemporary GPU, equivalent to for generative AI inference duties (for instance, serving a small language mannequin). The important thing benefit of MIG is its capacity to supply constant efficiency with hardware-level isolation. Every partition operates independently with its personal allotted reminiscence, computational cores, and SMs, ensuring that workloads don’t intervene with one another. This static allocation signifies that assets assigned to 1 occasion stay devoted to that occasion, to facilitate predictable efficiency and dependable useful resource administration.
Understanding the totally different MIG partitions
A MIG system consists of a single GPU “occasion” and a single Compute “occasion.” Every GPU occasion (GI) may also be additional sub-divided into a number of Compute Situations (CI) as required by customers. For instance, with a ml.p5en.48xlarge occasion, we will run the next find_MIG_profiles.yaml file to search out the out there profiles per H200 GPU:
This output lists the profiles out there to you. These versatile MIG profiles helps a variety of deployment situations, every optimized for various workload necessities and useful resource wants.
If we take a look at one of many profiles (say for instance 4g.71gb):
4g: represents the GI profile compute. This consists of SM assets.71gb: represents the GI profile reminiscence.
So on this case, we select profile 4g every with 71gb of GPU reminiscence!
Understanding MIG on Kubernetes
SageMaker HyperPod makes use of {custom} labels and the NVIDIA GPU Operator to handle MIG performance on Kubernetes (utilizing Amazon EKS). The GPU Operator makes use of the Kubernetes operator framework to automate the deployment and administration of NVIDIA software program parts wanted for GPU orchestration, with the NVIDIA MIG Supervisor being a mandatory element for MIG assist. This set up is completed along with the deployments, helm charts, and DaemonSets already put in by the HyperPodHelmCharts.
MIG on HyperPod EKS works via a label-based strategy. The MIG Supervisor, operating as a Kubernetes DaemonSet , screens nodes for particular MIG configuration labels. When these labels are detected, it mechanically configures the suitable MIG partitions utilizing MIG-parted. With the managed expertise (see extra within the following part), this course of is additional simplified—MIG configurations are managed on the occasion group degree, with HyperPod mechanically dealing with the required node labeling and configuration.
MIG assist on SageMaker HyperPod
Past these core MIG capabilities, SageMaker HyperPod helps improve the MIG expertise with its built-in enterprise options. The HyperPod resiliency options mechanically monitor cluster well being, detects and replaces defective {hardware}, and resumes workloads from checkpoints with out handbook intervention. HyperPod process governance offers fine-grained management over MIG useful resource allocation throughout groups, with computerized dealing with of priority-based useful resource reallocation. Moreover, complete one-click observability in HyperPod dashboards give directors full visibility into MIG occasion utilization, efficiency metrics, and useful resource allocation tendencies throughout the partitions. These capabilities assist organizations handle their MIG enabled clusters with enterprise-grade reliability, management, and transparency.
Answer overview
Earlier than organising MIG in your SageMaker HyperPod EKS cluster, confirm you may have the next:
- A SageMaker HyperPod cluster with Amazon EKS because the orchestrator. Should you haven’t created one but, confer with Making a SageMaker HyperPod cluster with Amazon EKS orchestration to arrange a HyperPod cluster.
- By default, the set up of the GPU Operator (extra particulars within the following part) is optionally available if you happen to arrange the cluster utilizing both the Fast setup or Customized setup.
- Overview the “Expertise 1” part on configuring a HyperPod EKS cluster with the MIG supervisor pre-installed.
- Should you didn’t allow MIG throughout cluster setup, don’t fear! The sections under additionally describe how one can set this up on an current cluster.
- By default, the set up of the GPU Operator (extra particulars within the following part) is optionally available if you happen to arrange the cluster utilizing both the Fast setup or Customized setup.
- Supported occasion out there so that you can use. For extra data on the supported GPU cases, confer with Supported MIG Profiles, and EC2 Accelerated Computing. You could use a Versatile Coaching Plan for this too.
- Applicable IAM permissions for cluster administration and MIG configuration. To study extra in regards to the permissions required, confer with AWS Identification and Entry Administration for SageMaker HyperPod.
Establishing MIG in your HyperPod cluster
On this part, we element how one can arrange MIG assist in your SageMaker HyperPod cluster. There are two experiences supported:
- Managed MIG expertise
- DIY expertise
The do-it-yourself (DIY) answer makes use of the Kubernetes command-line shopper kubectl, and a managed answer with Customized Labels is for straightforward configuration and utility of GPU partition labels. The DIY strategy operates on the occasion degree, whereas the managed answer operates on the occasion group degree.
Expertise 1: Managed MIG expertise (Really helpful)
The managed MIG expertise means that you can configure MIG in your HyperPod occasion teams. You utilize an AWS managed ConfigMap that’s mechanically arrange utilizing the AWS Managed GPU Operator set up in your HyperPod cluster. This expertise might be applied immediately utilizing the console (through the cluster arrange, or by utilizing add-ons), or utilizing the UpdateCluster API—with the assistance of Customized Labels.
Establishing new clusters
On this instance, we arrange a HyperPod EKS cluster utilizing the AWS Administration Console. In your SageMaker console, navigate to HyperPod Clusters, and select Create HyperPod cluster. Choose Orchestrated by Amazon EKS.
MIG is an optionally available configuration, in order of launch, it’s not enabled by default within the Fast setup part. To make use of the managed MIG expertise, select the Customized setup radio button.

In Customized setup, beneath Orchestration, verify the field for GPU Operator. Checking the GPU Operator field mechanically de-selects the NVIDIA system plugin field. The NVIDIA GPU Operator set up bundles with the set up of the Gadget Plugin, and so this verifies that there are not any double-installations or downstream dependency errors.
Subsequent, you may configure your occasion teams. This put up doesn’t cowl all the small print of the occasion group, besides the partition configuration.
In your occasion group configuration, beneath Superior configuration, activate Use GPU partition. This setting is utilized on the occasion group degree: the cases inside this occasion group can have partitioned GPUs. You possibly can select the MIG configuration you’d like. The configurations are organized into totally different partition classes:
- Low compute duties for light-weight duties that aren’t very compute intensive, equivalent to operating a number of iterative decodes.
- Excessive compute duties for duties that require compute or SM energy, equivalent to matrix multiplications (GEMM) for LLM prefill.
- Blended duties for operating various kinds of duties, equivalent to light-weight interactive growth duties alongside a number of inference duties, concurrently on a single GPU to maximise useful resource effectivity
One vital be aware is that equal-sized partitions divide every of your GPUs into the partitions of the identical kind, whereas blended partitions assist you to have totally different partitions in your GPUs. Please confer with the Understanding the totally different MIG partitions part above to grasp MIG partitions, together with what assets are cut up per partition.
For instance, if you happen to select the mixed-3-1g.18gb-1-4g.71gb profile, you get (inside a single GPU):
- 3 GPU cases, every with the
1gGPU occasion profile for compute, and18gbof HBM3e GPU reminiscence - 1 GPU occasion with the
3gGPU occasion profile for compute, and71gbof HBM3e GPU reminiscence - The UI may even show a visible depiction of how the GPUs are partitioned to your reference:
 |
You possibly can arrange the remainder of the cluster as you want. This put up doesn’t cowl the opposite segments of the cluster. For the remainder of this put up, until in any other case acknowledged, you might assume that we use a ml.p5en.48xlarge occasion with the MIG configuration acknowledged beforehand.
As soon as the cluster is InService, and your compute is in an Lively state inside your cluster, you might connect with your cluster. For extra data on that, take a look at these directions.
Should you run aws sagemaker describe-cluster --cluster-name $CLUSTER_NAME :
Particularly, discover the brand new KubernetesConfig parameter. That’s the place we will set MIG labels on the occasion group degree (utilizing UpdateCluster).
You may also confirm that MIG was setup accurately in your cluster by checking the MIG pods’ output:
This command confirms that the MIG supervisor is operating. Nevertheless, the success of MIG partitioning is mirrored within the occasion standing, the place MIG.standing is translated to the occasion standing. You possibly can observe how the standing transitions from “MIG partitioning in progress” to “Operating,” and the way errors are propagated via APIs and the console.
Establishing MIG on current clusters
When you have an current HyperPod cluster with out MIG assist, you may allow it utilizing the HyperPodHelmCharts. This offers a streamlined set up course of that handles the deployment of the required parts, together with the NVIDIA GPU Operator and MIG supervisor.
Set up the MIG supervisor parts utilizing the next command:
Once more, you may confirm the set up utilizing the same strategy because the earlier part.
Managing MIG configurations
There are two approaches to managing MIG configurations in your HyperPod cluster: occasion group degree administration via the UpdateCluster API and Customized Labels, and particular person occasion administration utilizing Kubernetes labels.
Occasion group degree administration
The UpdateCluster API lets you configure MIG profiles for the cases inside an occasion group:
This configuration:
- Applies to the cases in
MIG-group - Units up blended MIG profiles on every GPU
- Creates each
1g.18gband4g.71gbpartitions
Particular person occasion administration
For extra granular management inside an occasion group, you may handle MIG configurations on the particular person occasion degree utilizing Kubernetes labels. To allow MIG on a selected occasion, you may run the next command: kubectl label node $NODE nvidia.com/MIG.config=mixed-3-1g.18gb-1-4g.71gb --overwrite
In case you are utilizing the default ConfigMaps (extra on the ConfigMaps within the following Extra configuration particulars part, you too can take away MIG from an occasion as follows:
kubectl label node $NODE nvidia.com/MIG.congif=all-disabled --overwrite
To confirm whether or not the present MIG configuration of an occasion, you may run the next command:
kubectl describe node $NODE | grep "nvidia.com/MIG.*rely"
You might also use the HyperPod CLI, a command line software that helps handle clusters, coaching jobs, and inference endpoints on the SageMaker HyperPod clusters orchestrated by Amazon EKS, as follows:
hyp list-accelerator-partition-type
Whereas you should use kubectl label node to shortly allow MIG on a node to check, this strategy requires cautious consideration, as a result of your MIG configuration could possibly be misplaced in case a node is changed. If you’d like persistent MIG configurations, think about using the managed occasion group strategy, or confer with the next ConfigMap administration part on organising persistent ConfigMaps.
Expertise 2: DIY expertise
Whereas the managed expertise is really helpful, you too can arrange MIG assist manually utilizing the NVIDIA GPU Operator. This strategy offers foundational MIG performance via direct interplay with Kubernetes parts.
You possibly can set up immediately from the directions on the NVIDIA GPU Operator GitHub web page. Confirm that you simply set the devicePlugin.enabled flag to false, for the reason that HyperPodHelmCharts set up this for you as a part of the cluster arrange course of.
Key configuration parameters:
- MIG.technique=blended: Permits blended MIG profiles on GPUs.
- If sooner or later you’d like to alter between single and blended, you may patch the cluster coverage:
devicePlugin.enabled=false: Helps stop conflicts with the HyperPod default system plugin set upMIGManager.enabled=true: Permits the MIG supervisor elementMIGManager.WITH_REBOOT=true: Permits node reboots for MIG configuration adjustments
Not like the managed expertise (which is really helpful), this can’t be configured on the occasion group degree. This implies that you’ll want to make use of Kubernetes labels to handle the MIG lifecycle.
Whereas each approaches are supported, the managed expertise is really helpful, because it integrates seamlessly with enterprise options of SageMaker HyperPod like HyperPod process governance, Karpenter based mostly autoscaling, and one-click observability. For customers at present utilizing the DIY setup, migration to the managed expertise is simple, utilizing the steps outlined within the sub-sections above to be able to take full benefit of the automation and administration capabilities out there in SageMaker HyperPod.
Emigrate to the managed expertise, you may:
- Take away the DIY set up:
helm uninstall gpu-operator -n gpu-operator
- Set up the managed parts utilizing the HyperPod CLI (see Establishing MIG on current clusters).
The managed expertise offers extra advantages, together with:
- Occasion group degree configuration
- Integration with the options of HyperPod (equivalent to autoscaling)
- Simplified administration via HyperPod APIs, and a HyperPod managed CRD that’s up-to-date
Extra configuration particulars
The next sections embody extra particulars that could possibly be useful to you as you navigate MIG assist in your SageMaker HyperPod cluster.
Accessible MIG profiles
Along with operating the nvidia-smi instructions (or the offered find_MIG_profiles.yaml manifest), yow will discover a complete record of supported MIG partitions and their specs throughout totally different GPU architectures (together with Ampere, Hopper, and Blackwell) in NVIDIA’s official MIG documentation.
ConfigMap administration
Each DIY and managed MIG implementations use Kubernetes ConfigMaps to outline out there MIG profiles. You possibly can view the default configurations utilizing:
The NVIDIA default configuration (default-MIG-parted-config) consists of solely single-partition profiles by default, whereas the AWS managed configuration (default-MIG-config) consists of each single and blended profiles out of the field.
Should you want a profile that isn’t included within the default configurations, you may create a {custom} ConfigMap.
Confirm that the {custom} profile you’re configuring is supported (confer with the Accessible MIG profiles part).
To make use of your {custom} configuration, apply the ConfigMap and replace the MIG supervisor to make use of your {custom} config:
As a substitute of utilizing the default-MIG-parted-config (or default-MIG-config for the managed set up), you’re pointing the MIG supervisor to your {custom} ConfigMap. Which means the MIG supervisor will now solely see the profiles that you simply’ve set on this ConfigMap, so proceed with warning.
MIG operations information
The next are some helpful instructions to configure and handle the lifecycle of MIG in your SageMaker HyperPod cluster. Allow MIG with a selected profile:
Disable MIG:
Profile verification:
Monitor MIG parts:
Confirm GPU partitioning:
Palms-on examples
To exhibit these ideas in motion, let’s discover some sensible examples: We’ll present methods to run concurrent inference workloads utilizing MIG partitions, showcasing the advantages of useful resource isolation and parallel deployment. Then, we’ll exhibit organising interactive growth environments (JupyterLab notebooks), every with entry to solely the GIs assigned to them, illustrating how knowledge scientists can effectively share GPU assets for experimentation and growth. This part is optionally available.
For the examples under, we’ll use the identical cluster with one ml.p5en.48xlarge, with the next MIG profile: mixed-3-1g.18gb-1-4g.71gb.
Operating concurrent workloads with MIG
On this part, we’ll exhibit how MIG assist on SageMaker HyperPod permits environment friendly useful resource utilization throughout totally different ML workload sorts. We’ll use the identical pre-configured HyperPod EKS cluster with an occasion group with just one ml.p5en.48xlarge occasion. The occasion is configured with the next MIG profile:
Notice: Please think about your SLAs and buyer wants to your deployments. The examples proven under are to be thought of solely for example.
We’ll exhibit three distinct workload sorts operating concurrently on the identical occasion to showcase the flexibleness of MIG:
- Inference operator deployment: Deploy a mannequin from SageMaker JumpStart
- NVIDIA Dynamo deployment: Implement disaggregated inference with separate prefill and decode phases
- Interactive deployment: Run a Jupyter Pocket book setting on a MIG partition
Along with deployments, we speak via integrations with HyperPod one-click observability dashboards and HyperPod process governance, which offer detailed insights into MIG partition utilization, and assist you to optimize cluster utilization respectively.
Workload 1: SageMaker HyperPod Inference Operator
The SageMaker HyperPod Inference Operator offers a streamlined, production-ready answer for deploying inference workloads in your HyperPod cluster. As a totally managed element, it handles the complexities of mannequin deployment, scaling, and monitoring whereas seamlessly integrating with MIG for optimum useful resource utilization.
With MIG assist, the Inference Operator intelligently maps mannequin deployments to appropriately sized GPU partitions, enabling environment friendly multi-model serving on a single GPU. This integration delivers a number of key advantages:
- Useful resource optimization: Deploy a number of fashions throughout MIG partitions based mostly on their computational wants
- Workload isolation: Facilitate constant efficiency with hardware-level isolation between mannequin endpoints
- Automated administration: Use built-in scaling and monitoring capabilities in HyperPod
- Enterprise-grade reliability: Profit from computerized fault detection and restoration
- Simplified operations: Handle deployments via acquainted Kubernetes interfaces
On this instance, we’ll deploy the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B mannequin, an environment friendly distilled mannequin that demonstrates robust reasoning capabilities whereas being compact sufficient to run on smaller MIG partitions. We’ll use the JumpStartModels Kubernetes Customized Useful resource Definition (CRD), which simplifies deployment of pre-built fashions from SageMaker JumpStart.
The inference operator additionally means that you can deploy fashions from Amazon S3. Nevertheless, on this instance we’ll give attention to solely the JumpStartModels CRD.
Create a deployment manifest that specifies the mannequin and the MIG configuration:
You possibly can monitor the standing of the deployment:kubectl describe jumpstartmodel -n ds-model-deployment deepseek-jumpstartA profitable deployment will present:
As soon as deployed, you may invoke the mannequin via both the SageMaker endpoint, or the Software Load Balancer (ALB), each of that are auto deployed by the SageMaker HyperPod Inference Operator. Right here’s an instance of utilizing the SageMaker endpoint:
An instance output appears like:
As a substitute of utilizing native Kubernetes manifests and CRDs, you may additionally decide to make use of the HyperPod CLI. An instance command for a JumpStart deployment appears like:
The HyperPod Inference Operator, via HyperPod Autoscaling (Kubernetes Occasion Pushed Autoscaling), additionally means that you can scale your deployment. For instance, you might scale your deployment up to make use of a number of MIG profiles (similar deployment) to deal with demand out of your finish customers. Right here’s an instance manifest that you could be use with KEDA Autoscaling to scale as much as 16 replicas. Along with scaling, the HyperPod Inference Operator additionally helps Clever request Routing, and KV cache with MIG.
You may also deploy your JumpStart mannequin immediately from SageMaker AI Studio, as proven within the following screenshot:

The next is an outline of three distinct workloads operating on one occasion. The primary workload is a dynamically scaling deployment of the deepseek-llm-r1-distill-qwen-1-5b mannequin, dealt with by the HyperPod Inference Operator. The second workload is a static deployment (disaggregated throughout two MIG profiles) of the Qwen3-0.6B mannequin, and the final one exhibits Jupyter notebooks popping up based mostly on requests from knowledge scientists.

Workload 2: Static deployment of Qwen3-0.6B for inside customers
The second workload we deploy on our ml.p5en.48xlarge occasion for demonstration functions is a static deployment of the Qwen3-0.6B mannequin. It is a static deployment for inside customers solely, and we make the most of an open supply server, that helps disaggregated inference.
LLM inference consists of two distinct phases with totally different computational traits. The prefill part processes the enter immediate to generate the KV cache. This course of includes loads of matrix multiplications, and is subsequently compute-intensive (require entry to extra SMs). Then again, the decode part is much more reminiscence/bandwidth/IO intensive, because it generates tokens sequentially (requires adequate reminiscence for KV cache storage). This distinct useful resource profile makes disaggregated inference notably well-suited for MIG deployments. By matching every part to appropriately sized MIG partitions, we will optimize useful resource utilization:
- Prefill staff: Bigger partitions (4g.71gb) with extra SMs for compute-intensive operations
- Decode staff: Smaller partitions (1g.18gb) with adequate reminiscence however fewer SMs
Utilizing vLLM as our backend, we’ll exhibit methods to configure this tradition deployment on HyperPod. For this pattern, we deploy the Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B mannequin. We observe the deployment directions from NVIDIA’s and vLLM’s documentation (1, 2, 3).
You should use the next disagg.yaml file focused to make use of the MIG profiles on our occasion.
This deployment creates:
- One frontend service for request routing
- Two decode staff utilizing
1g.18gbMIG partitions for environment friendly token technology - One prefill employee utilizing a
4g.71gbMIG partition for compute-intensive immediate processing
To grasp the CRDs utilized by NVIDIA (DynamoGraphDeployments), confer with Understanding Dynamo’s Customized Sources. You possibly can invoke the mannequin via the frontend service (utilizing port-forwarding)
An output would appear like:
Notice that that is simply an instance and it’s not meant to be a manufacturing workload. Along with contemplating your SLAs, please configure your ALB with an HTTPS listener and a TLS certificates. This pattern makes use of HTTP for simplicity. Moreover, the hf-token-secret on this pattern is saved as an setting variable (and by extension, in your terminal historical past). We advocate encrypting your Kubernetes secrets and techniques utilizing AWS KMS.
Workload 3: Interactive workloads on a Jupyter pocket book
The ultimate instance demonstrates how knowledge scientists can leverage MIG partitions for interactive growth environments. We’ll create a growth house utilizing one among our 1g.18gb partitions, offering devoted GPU assets for experimentation and growth whereas sustaining isolation from different workloads. This weblog put up assumes that you simply’ve arrange the house operator. For extra data on how to try this, confer with this documentation.
Let’s create an area manifest utilizing the nvidia.com/MIG-1g.18gb MIG profile.
You possibly can deploy the house utilizingkubectl apply -f house.yamlYou might also use the HyperPod CLI to create this house:
As soon as the house is operating, you may entry it via port forwarding:kubectl port-forward service/data-scientist-space-MIG-service 8888:8888
You must also see this house operating in your console. As soon as in your pocket book, you may run nvidia-smi -L or simply nvidia-smi to point out you your allotted GPU (partition):
This setup offers knowledge scientists with:
- Devoted GPU assets for growth
- Isolation from manufacturing workloads
- Entry to acquainted Jupyter environments
- Environment friendly useful resource utilization via MIG partitioning
The identical strategy can be utilized to assist a number of builders, every with their very own remoted MIG partition, maximizing the utility of your GPU infrastructure whereas sustaining efficiency assurances.
Now that the three workloads are operating concurrently on totally different MIG partitions, we will see the ability of MIG-enabled useful resource sharing:
SageMaker HyperPod Observability
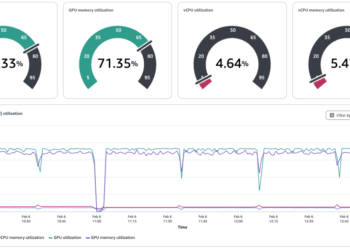
One-click observability in HyperPod offers complete insights into MIG partition utilization via pre-configured Grafana dashboards. These dashboards supply:
- Actual-time monitoring of GPU utilization per MIG partition
- Reminiscence utilization monitoring throughout totally different workloads
- Useful resource allocation visualization
- Efficiency metrics for inference endpoints
- Automated alerts for useful resource constraints
The next is an instance of the observability dashboard that shows partition utilization.

SageMaker HyperPod process governance
With SageMaker HyperPod process governance, clients can optimize Amazon SageMaker HyperPod cluster utilization on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS), distribute truthful utilization, and assist environment friendly useful resource allocation throughout totally different groups or tasks.
As with current performance, you may allow process prioritization and fair-share useful resource allocation via cluster insurance policies that prioritize crucial workloads and distribute idle compute throughout groups. Through the use of HyperPod process governance, you may outline queue admission insurance policies (first-come-first-serve by default or process rating) and idle compute allocation strategies (first-come-first-serve or fair-share by default). Within the Compute quota allocation coverage, you may create and edit allocations to distribute assets amongst groups, allow lending and borrowing of idle compute, configure preemption of low-priority duties, and assign fair-share weights.
The important thing innovation is within the ComputeQuotaResourceConfig, the place you’ll now discover fine-grained choices for useful resource allocation. Along with the present instance-level quotas, GPU-level quota, now you can immediately specify MIG partition quotas by occasion kind and household or by {hardware} kind. Whenever you outline GPU allocations, HyperPod process governance intelligently calculates acceptable default values for vCPUs and reminiscence that are set proportionally. You possibly can change default values based mostly in your wants.
These hands-on examples exhibit how MIG assist on SageMaker HyperPod helps environment friendly useful resource sharing throughout totally different workload sorts. By way of hardware-level isolation and versatile useful resource partitioning, organizations can maximize their GPU infrastructure funding whereas sustaining workload efficiency and reliability. The combination with the great function set of HyperPod offers end-to-end assist for ML operations:
Clear up
Should you adopted together with the weblog, and would really like directions on cleansing up your assets, confer with Deleting a SageMaker HyperPod cluster.
Conclusion
On this put up, we launched Multi-Occasion GPU (MIG) assist for Amazon SageMaker HyperPod, a strong functionality that permits organizations to maximise their GPU infrastructure funding via versatile useful resource partitioning. By operating a number of remoted duties concurrently on a single GPU, MIG addresses key challenges in ML infrastructure administration, from value optimization to useful resource utilization.
With the SageMaker HyperPod managed MIG expertise, you may:
- Optimize GPU utilization by operating a number of workloads concurrently
- Allow predictable efficiency via hardware-level isolation
- Scale ML operations effectively throughout groups and workloads
- Cut back infrastructure prices by right-sizing GPU assets
- Keep enterprise-grade safety and governance
The combination of MIG with the present options of HyperPod—together with process governance, observability, and automatic resiliency—offers a complete answer for managing complicated ML duties at scale. Should you’re serving a number of inference endpoints, supporting growth groups, performing scientific analysis, or optimizing coaching or reinforcement studying workflows, MIG on SageMaker HyperPod presents the flexibleness and management wanted to satisfy your group’s ML infrastructure wants whereas decreasing growth prices, and rising mixture useful resource utilization.
To get began with MIG on SageMaker HyperPod, go to the SageMaker HyperPod documentation or discover our hands-on workshop. For extra details about SageMaker HyperPod and its options, take a look at SageMaker HyperPod.
A particular because of our colleagues Giuseppe Angelo Porcelli (Principal Machine Studying Specialist SA), Marta Aleszewicz (Sr. SDE), Ashish Sharma (Sr. SDE), Satish Gollaprolu (SDE), Shantanu Tripathi (SDE), Yun-Chi Chen (UX Designer) and others on the SageMaker AI workforce for his or her assist within the launch of this functionality.
Concerning the authors
 Aman Shanbhag is a Specialist Options Architect on the ML Frameworks workforce at Amazon Net Providers (AWS), the place he helps clients and companions with deploying ML coaching and inference options at scale. Earlier than becoming a member of AWS, Aman graduated from Rice College with levels in laptop science, arithmetic, and entrepreneurship.
Aman Shanbhag is a Specialist Options Architect on the ML Frameworks workforce at Amazon Net Providers (AWS), the place he helps clients and companions with deploying ML coaching and inference options at scale. Earlier than becoming a member of AWS, Aman graduated from Rice College with levels in laptop science, arithmetic, and entrepreneurship.
 Siamak Nariman is a Senior Product Supervisor at AWS. He’s centered on AI/ML know-how, ML mannequin administration, and ML governance to enhance general organizational effectivity and productiveness. He has in depth expertise automating processes and deploying varied applied sciences.
Siamak Nariman is a Senior Product Supervisor at AWS. He’s centered on AI/ML know-how, ML mannequin administration, and ML governance to enhance general organizational effectivity and productiveness. He has in depth expertise automating processes and deploying varied applied sciences.
 Anoop Saha is a Sr GTM Specialist at Amazon Net Providers (AWS) specializing in generative AI mannequin coaching and inference. He companions with prime frontier mannequin builders, strategic clients, and AWS service groups to allow distributed coaching and inference at scale on AWS and lead joint GTM motions. Earlier than AWS, Anoop held a number of management roles at startups and enormous companies, primarily specializing in silicon and system structure of AI infrastructure.
Anoop Saha is a Sr GTM Specialist at Amazon Net Providers (AWS) specializing in generative AI mannequin coaching and inference. He companions with prime frontier mannequin builders, strategic clients, and AWS service groups to allow distributed coaching and inference at scale on AWS and lead joint GTM motions. Earlier than AWS, Anoop held a number of management roles at startups and enormous companies, primarily specializing in silicon and system structure of AI infrastructure.
 Ankit Anand is a Principal Basis Fashions Go-To-Market (GTM) Specialist at AWS. He companions with prime generative AI mannequin builders, strategic clients, and AWS Service Groups to allow the subsequent technology of AI/ML workloads on AWS. Ankit’s expertise consists of product administration experience throughout the monetary providers trade for high-frequency/low-latency buying and selling and enterprise growth for Amazon Alexa.
Ankit Anand is a Principal Basis Fashions Go-To-Market (GTM) Specialist at AWS. He companions with prime generative AI mannequin builders, strategic clients, and AWS Service Groups to allow the subsequent technology of AI/ML workloads on AWS. Ankit’s expertise consists of product administration experience throughout the monetary providers trade for high-frequency/low-latency buying and selling and enterprise growth for Amazon Alexa.
 Sivashankar, Software program Engineering Supervisor at Amazon Net Providers (AWS), leads a workforce in HyperPod that’s liable for HyperPod Job Governance, Fractional GPU, and SageMaker Make clear. Sivashankar has in depth expertise in AWS main EKS management airplane providers and Amazon MQ for RabbitMQ and a protracted profession at Microsoft, the place he helped form Microsoft 365 experiences.
Sivashankar, Software program Engineering Supervisor at Amazon Net Providers (AWS), leads a workforce in HyperPod that’s liable for HyperPod Job Governance, Fractional GPU, and SageMaker Make clear. Sivashankar has in depth expertise in AWS main EKS management airplane providers and Amazon MQ for RabbitMQ and a protracted profession at Microsoft, the place he helped form Microsoft 365 experiences.
 Pradeep Cruz is a Senior SDM at Amazon Net Providers (AWS), driving AI infrastructure and purposes at enterprise scale. Main cross-functional organizations at Amazon SageMaker AI, he has constructed and scaled a number of high-impact providers for enterprise clients together with SageMaker HyperPod-EKS Inference, Job Governance, Characteristic Retailer, AIOps, and JumpStart Mannequin Hub at AWS, alongside enterprise AI techniques at T-Cellular and Ericsson. His technical depth spans distributed techniques, GenAI/ML, Kubernetes, cloud computing, and full-stack software program growth.
Pradeep Cruz is a Senior SDM at Amazon Net Providers (AWS), driving AI infrastructure and purposes at enterprise scale. Main cross-functional organizations at Amazon SageMaker AI, he has constructed and scaled a number of high-impact providers for enterprise clients together with SageMaker HyperPod-EKS Inference, Job Governance, Characteristic Retailer, AIOps, and JumpStart Mannequin Hub at AWS, alongside enterprise AI techniques at T-Cellular and Ericsson. His technical depth spans distributed techniques, GenAI/ML, Kubernetes, cloud computing, and full-stack software program growth.