As AWS environments develop in complexity, troubleshooting points with sources can change into a frightening job. Manually investigating and resolving issues may be time-consuming and error-prone, particularly when coping with intricate techniques. Luckily, AWS supplies a robust device referred to as AWS Assist Automation Workflows, which is a group of curated AWS Techniques Supervisor self-service automation runbooks. These runbooks are created by AWS Assist Engineering with finest practices discovered from fixing buyer points. They allow AWS prospects to troubleshoot, diagnose, and remediate frequent points with their AWS sources.
Amazon Bedrock is a completely managed service that provides a selection of high-performing basis fashions (FMs) from main AI corporations like AI21 Labs, Anthropic, Cohere, Meta, Mistral AI, Stability AI, and Amazon via a single API, together with a broad set of capabilities to construct generative AI functions with safety, privateness, and accountable AI. Utilizing Amazon Bedrock, you’ll be able to experiment with and consider high FMs in your use case, privately customise them along with your knowledge utilizing strategies corresponding to fine-tuning and Retrieval Augmented Technology (RAG), and construct brokers that execute duties utilizing your enterprise techniques and knowledge sources. As a result of Amazon Bedrock is serverless, you don’t need to handle infrastructure, and you’ll securely combine and deploy generative AI capabilities into your functions utilizing the AWS companies you might be already acquainted with.
On this put up, we discover the right way to use the ability of Amazon Bedrock Brokers and AWS Assist Automation Workflows to create an clever agent able to troubleshooting points with AWS sources.
Resolution overview
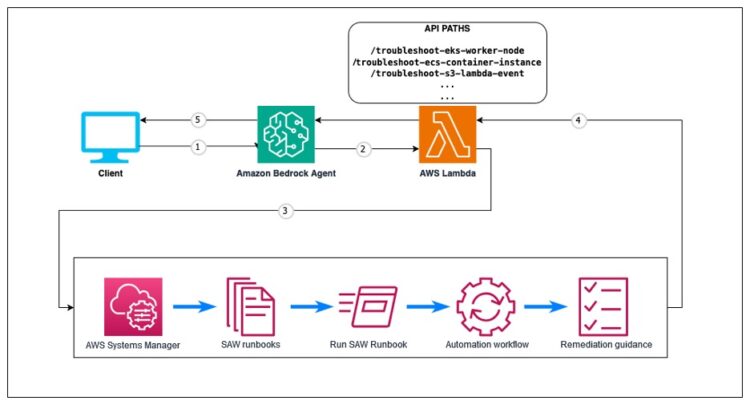
Though the answer is flexible and may be tailored to make use of a wide range of AWS Assist Automation Workflows, we give attention to a selected instance: troubleshooting an Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) employee node that failed to hitch a cluster. The next diagram supplies a high-level overview of troubleshooting brokers with Amazon Bedrock.

Our answer is constructed across the following key parts that work collectively to offer a seamless and environment friendly troubleshooting expertise:
- Amazon Bedrock Brokers – Amazon Bedrock Brokers acts because the clever interface between customers and AWS Assist Automation Workflows. It processes pure language queries to know the difficulty context and manages dialog movement to collect required data. The agent makes use of Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 Sonnet mannequin for superior reasoning and response technology, enabling pure interactions all through the troubleshooting course of.
- Amazon Bedrock agent motion teams – These motion teams outline the structured API operations that the Amazon Bedrock agent can invoke. Utilizing OpenAPI specs, they outline the interface between the agent and AWS Lambda features, specifying the out there operations, required parameters, and anticipated responses. Every motion group comprises the API schema that tells the agent the right way to correctly format requests and interpret responses when interacting with Lambda features.
- Lambda Operate – The Lambda operate acts as the combination layer between the Amazon Bedrock agent and AWS Assist Automation Workflows. It validates enter parameters from the agent and initiates the suitable SAW runbook execution. It displays the automation progress whereas processing the technical output right into a structured format. When the workflow is full, it returns formatted outcomes again to the agent for person presentation.
- IAM position – The AWS Id and Entry Administration (IAM) position supplies the Lambda operate with the required permissions to execute AWS Assist Automation Workflows and work together with required AWS companies. This position follows the precept of least privilege to keep up safety finest practices.
- AWS Assist Automation Workflows – These pre-built diagnostic runbooks are developed by AWS Assist Engineering. The workflows execute complete system checks based mostly on AWS finest practices in a standardized, repeatable method. They cowl a variety of AWS companies and customary points, encapsulating AWS Assist’s in depth troubleshooting experience.
The next steps define the workflow of our answer:
- Customers begin by describing their AWS useful resource difficulty in pure language via the Amazon Bedrock chat console. For instance, “Why isn’t my EKS employee node becoming a member of the cluster?”
- The Amazon Bedrock agent analyzes the person’s query and matches it to the suitable motion outlined in its OpenAPI schema. If important data is lacking, corresponding to a cluster identify or occasion ID, the agent engages in a pure dialog to collect the required parameters. This makes certain that crucial knowledge is collected earlier than continuing with the troubleshooting workflow.
- The Lambda operate receives the validated request and triggers the corresponding AWS Assist Automation Workflow. These SAW runbooks include complete diagnostic checks developed by AWS Assist Engineering to establish frequent points and their root causes. The checks run robotically with out requiring person intervention.
- The SAW runbook systematically executes its diagnostic checks and compiles the findings. These outcomes, together with recognized points and configuration issues, are structured in JSON format and returned to the Lambda operate.
- The Amazon Bedrock agent processes the diagnostic outcomes utilizing chain of thought (CoT) reasoning, based mostly on the ReAct (synergizing reasoning and appearing) method. This allows the agent to research the technical findings, establish root causes, generate clear explanations, and supply step-by-step remediation steerage.
In the course of the reasoning part of the agent, the person is ready to view the reasoning steps.
Troubleshooting examples
Let’s take a better have a look at a standard difficulty we talked about earlier and the way our agent can help in troubleshooting it.
EKS employee node failed to hitch EKS cluster
When an EKS employee node fails to hitch an EKS cluster, our Amazon Bedrock agent may be invoked with the related data: cluster identify and employee node ID. The agent will execute the corresponding AWS Assist Automation Workflow, which can carry out checks like verifying the employee node’s IAM position permissions and verifying the required community connectivity.
The automation workflow will run all of the checks. Then Amazon Bedrock agent will ingest the troubleshooting, clarify the basis reason behind the difficulty to the person, and recommend remediation steps based mostly on the AWSSupport-TroubleshootEKSWorkerNode output, corresponding to updating the employee node’s IAM position or resolving community configuration points, enabling them to take the required actions to resolve the issue.
OpenAPI instance
Whenever you create an motion group in Amazon Bedrock, you could outline the parameters that the agent must invoke from the person. You can too outline API operations that the agent can invoke utilizing these parameters. To outline the API operations, we’ll create an OpenAPI schema in JSON:
"Body_troubleshoot_eks_worker_node_troubleshoot_eks_worker_node_post": {
"properties": {
"cluster_name": {
"kind": "string",
"title": "Cluster Identify",
"description": "The identify of the EKS cluster"
},
"worker_id": {
"kind": "string",
"title": "Employee Id",
"description": "The ID of the employee node"
}
},
"kind": "object",
"required": [
"cluster_name",
"worker_id"
],
"title": "Body_troubleshoot_eks_worker_node_troubleshoot_eks_worker_node_post"
}
The schema consists of the next parts:
- Body_troubleshoot_eks_worker_node_troubleshoot_eks_worker_node_post – That is the identify of the schema, which corresponds to the request physique for the
troubleshoot-eks-worker_nodePOST endpoint. - Properties – This part defines the properties (fields) of the schema:
- “cluster_name” – This property represents the identify of the EKS cluster. It’s a string kind and has a title and outline.
- “worker_id” – This property represents the ID of the employee node. It’s also a string kind and has a title and outline.
- Kind – This property specifies that the schema is an “object” kind, which means it’s a assortment of key-value pairs.
- Required – This property lists the required fields for the schema, which on this case are “cluster_name” and “employee _id”. These fields should be offered within the request physique.
- Title – This property supplies a human-readable title for the schema, which can be utilized for documentation functions.
The OpenAPI schema defines the construction of the request physique. To be taught extra, see Outline OpenAPI schemas in your agent’s motion teams in Amazon Bedrock and OpenAPI specification.
Lambda operate code
Now let’s discover the Lambda operate code:
@app.put up("/troubleshoot-eks-worker-node")
@tracer.capture_method
def troubleshoot_eks_worker_node(
cluster_name: Annotated[str, Body(description="The name of the EKS cluster")],
worker_id: Annotated[str, Body(description="The ID of the worker node")]
) -> dict:
"""
Troubleshoot EKS employee node that failed to hitch the cluster.
Args:
cluster_name (str): The identify of the EKS cluster.
worker_id (str): The ID of the employee node.
Returns:
dict: The output of the Automation execution.
"""
return execute_automation(
automation_name="AWSSupport-TroubleshootEKSWorkerNode",
parameters={
'ClusterName': [cluster_name],
'WorkerID': [worker_id]
},
execution_mode="TroubleshootWorkerNode"
)
The code consists of the next parts
- app.put up(“/troubleshoot-eks-worker-node”, description=”Troubleshoot EKS employee node failed to hitch the cluster”) – It is a decorator that units up a route for a POST request to the
/troubleshoot-eks-worker-nodeendpoint. The outline parameter supplies a quick clarification of what this endpoint does. - @tracer.capture_method – That is one other decorator that’s doubtless used for tracing or monitoring functions, probably as a part of an utility efficiency monitoring (APM) device. It captures details about the execution of the operate, such because the period, errors, and different metrics.
- cluster_name: str = Physique(description=”The identify of the EKS cluster”), – This parameter specifies that the
cluster_nameis a string kind and is predicted to be handed within the request physique. The Physique decorator is used to point that this parameter ought to be extracted from the request physique. The outline parameter supplies a quick clarification of what this parameter represents. - worker_id: str = Physique(description=”The ID of the employee node”) – This parameter specifies that the
worker_idis a string kind and is predicted to be handed within the request physique. - -> Annotated[dict, Body(description=”The output of the Automation execution”)] – That is the return kind of the operate, which is a dictionary. The Annotated kind is used to offer extra metadata in regards to the return worth, particularly that it ought to be included within the response physique. The outline parameter supplies a quick clarification of what the return worth represents.
To hyperlink a brand new SAW runbook within the Lambda operate, you’ll be able to observe the identical template.
Conditions
Be sure to have the next conditions:
Deploy the answer
Full the next steps to deploy the answer:
- Clone the GitHub repository and go to the basis of your downloaded repository folder:
$ git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/sample-bedrock-agent-for-troubleshooting-aws-resources.git$ cd bedrock-agent-for-troubleshooting-aws-resources- Set up native dependencies:
$ npm set up- Sign up to your AWS account utilizing the AWS CLI by configuring your credential file (substitute
with the profile identify of your deployment AWS account):
$ export AWS_PROFILE=PROFILE_NAME- Bootstrap the AWS CDK surroundings (it is a one-time exercise and isn’t wanted in case your AWS account is already bootstrapped):
$ cdk bootstrap- Run the script to switch the placeholders in your AWS account and AWS Area within the config recordsdata:
$ cdk deploy --allTake a look at the agent
Navigate to the Amazon Bedrock Brokers console in your Area and discover your deployed agent. You’ll discover the agent ID within the cdk deploy command output.
Now you can work together with the agent and take a look at troubleshooting a employee node not becoming a member of an EKS cluster. The next are some instance questions:
- I need to troubleshoot why my Amazon EKS employee node isn’t becoming a member of the cluster. Are you able to assist me?
- Why this occasion isn’t capable of be part of the EKS cluster
?
The next screenshot exhibits the console view of the agent.

The agent understood the query and mapped it with the appropriate motion group. It additionally noticed that the parameters wanted are lacking within the person immediate. It got here again with a follow-up query to require the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) occasion ID and EKS cluster identify.

We will see the agent’s thought course of within the hint step 1. The agent assesses the following step as able to name the appropriate Lambda operate and proper API path.

With the outcomes getting back from the runbook, the agent now evaluations the troubleshooting final result. It goes via the knowledge and can begin writing the answer the place it supplies the directions for the person to observe.
Within the reply offered, the agent was capable of spot all the problems and remodel that into answer steps. We will additionally see the agent mentioning the appropriate data like IAM coverage and the required tag.
Clear up
When implementing Amazon Bedrock Brokers, there are not any extra prices for useful resource building. Nevertheless, prices are incurred for embedding mannequin and textual content mannequin invocations on Amazon Bedrock, with prices based mostly on the pricing of every FM used. On this use case, additionally, you will incur prices for Lambda invocations.
To keep away from incurring future prices, delete the created sources by the AWS CDK. From the basis of your repository folder, run the next command:
$ npm run cdk destroy --allConclusion
Amazon Bedrock Brokers and AWS Assist Automation Workflows are highly effective instruments that, when mixed, can revolutionize AWS useful resource troubleshooting. On this put up, we explored a serverless utility constructed with the AWS CDK that demonstrates how these applied sciences may be built-in to create an clever troubleshooting agent. By defining motion teams inside the Amazon Bedrock agent and associating them with particular situations and automation workflows, we’ve developed a extremely environment friendly course of for diagnosing and resolving points corresponding to Amazon EKS employee node failures.
Our answer showcases the potential for automating advanced troubleshooting duties, saving time and streamlining operations. Powered by Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 Sonnet, the agent demonstrates improved understanding and responding in languages apart from English, corresponding to French, Japanese, and Spanish, making it accessible to international groups whereas sustaining its technical accuracy and effectiveness. The clever agent shortly identifies root causes and supplies actionable insights, whereas robotically executing related AWS Assist Automation Workflows. This strategy not solely minimizes downtime, but additionally scales successfully to accommodate numerous AWS companies and use circumstances, making it a flexible basis for organizations seeking to improve their AWS infrastructure administration.
Discover the AWS Assist Automation Workflow for added use circumstances and think about using this answer as a place to begin for constructing extra complete troubleshooting brokers tailor-made to your group’s wants. To be taught extra about utilizing brokers to orchestrate workflows, see Automate duties in your utility utilizing conversational brokers. For particulars about utilizing guardrails to safeguard your generative AI functions, seek advice from Cease dangerous content material in fashions utilizing Amazon Bedrock Guardrails.
Comfortable coding!
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all of the reviewers for his or her precious suggestions.
In regards to the Authors
 Wael Dimassi is a Technical Account Supervisor at AWS, constructing on his 7-year background as a Machine Studying specialist. He enjoys studying about AWS AI/ML companies and serving to prospects meet their enterprise outcomes by constructing options for them.
Wael Dimassi is a Technical Account Supervisor at AWS, constructing on his 7-year background as a Machine Studying specialist. He enjoys studying about AWS AI/ML companies and serving to prospects meet their enterprise outcomes by constructing options for them.
 Marwen Benzarti is a Senior Cloud Assist Engineer at AWS Assist the place he makes a speciality of Infrastructure as Code. With over 4 years at AWS and a pair of years of earlier expertise as a DevOps engineer, Marwen works intently with prospects to implement AWS finest practices and troubleshoot advanced technical challenges. Outdoors of labor, he enjoys taking part in each aggressive multiplayer and immersive story-driven video video games.
Marwen Benzarti is a Senior Cloud Assist Engineer at AWS Assist the place he makes a speciality of Infrastructure as Code. With over 4 years at AWS and a pair of years of earlier expertise as a DevOps engineer, Marwen works intently with prospects to implement AWS finest practices and troubleshoot advanced technical challenges. Outdoors of labor, he enjoys taking part in each aggressive multiplayer and immersive story-driven video video games.