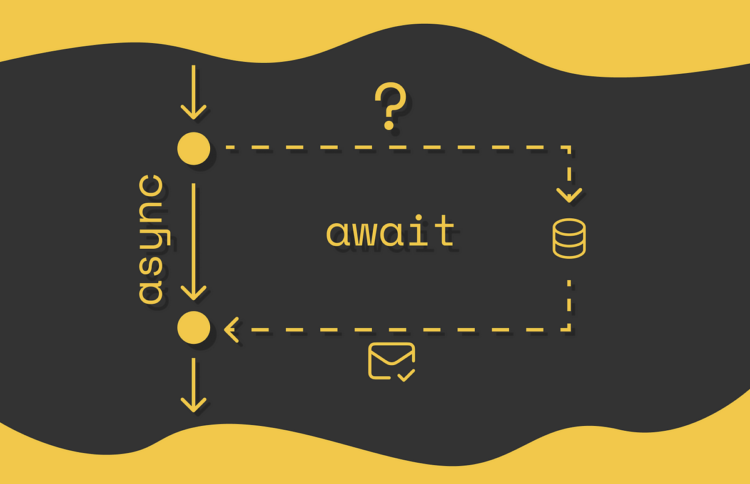
Designing asynchronous pipelines for environment friendly knowledge processing
Notice. This text already assumes that you’re conversant in callbacks, guarantees, and have a primary understanding of the asynchronous paradigm in JavaScript.
The asynchronous mechanism is among the most necessary ideas in JavaScript and programming usually. It permits a program to individually execute secondary duties within the background with out blocking the present thread from executing major duties. When a secondary job is accomplished, its result’s returned and this system continues to run usually. On this context, such secondary duties are referred to as asynchronous.
Asynchronous duties sometimes embrace making requests to exterior environments like databases, internet APIs or working programs. If the results of an asynchronous operation doesn’t have an effect on the logic of the principle program, then as an alternative of simply ready earlier than the duty can have accomplished, it’s a lot better to not waste this time and proceed executing major duties.
Nonetheless, typically the results of an asynchronous operation is used instantly within the subsequent code strains. In such circumstances, the succeeding code strains shouldn’t be executed till the asynchronous operation is accomplished.
Notice. Earlier than attending to the principle a part of this text, I want to present the motivation for why asynchronicity is taken into account an necessary matter in Knowledge Science and why I used JavaScript as an alternative of Python to clarify the
async / awaitsyntax.
Knowledge engineering is an inseparable a part of Knowledge Science, which primarily consists of designing strong and environment friendly knowledge pipelines. One of many typical duties in knowledge engineering consists of making common calls to APIs, databases, or different sources to retrieve knowledge, course of it, and retailer it someplace.
Think about a knowledge supply that encounters community points and can’t return the requested knowledge instantly. If we merely make the request in code to that service, we must wait fairly a bit, whereas doing nothing. Wouldn’t it’s higher to keep away from wasting your processor time and execute one other operate, for instance? That is the place the facility of asynchronicity comes into play, which would be the central matter of this text!
No one will deny the truth that Python is the most well-liked present selection for creating Knowledge Science purposes. Nonetheless, JavaScript is one other language with an enormous ecosystem that serves varied growth functions, together with constructing internet purposes that course of knowledge retrieved from different companies. Because it seems, asynchronicity performs one of the elementary roles in JavaScript.
Moreover, in comparison with Python, JavaScript has richer built-in assist for coping with asynchronicity and often serves as a greater instance to dive deeper into this matter.
Lastly, Python has an analogous async / await building. Subsequently, the knowledge introduced on this article about JavaScript may also be transferable to Python for designing environment friendly knowledge pipelines.
Within the first variations of JavaScript, asynchronous code was primarily written with callbacks. Sadly, it led builders to a widely known drawback named “callback hell”. A number of instances asynchronous code written with uncooked callbacks led to a number of nested code scopes which have been extraordinarily troublesome to learn. That’s the reason in 2012 the JavaScript creators launched guarantees.
// Instance of the "callback hell" drawbackfunctionOne(operate () {
functionTwo(operate () {
functionThree(operate () {
functionFour(operate () {
...
});
});
});
});
Guarantees present a handy interface for asynchronous code growth. A promise takes right into a constructor an asynchronous operate which is executed at a sure second of time sooner or later. Earlier than the operate is executed, the promise is alleged to be in a pending state. Relying on whether or not the asynchronous operate has been accomplished efficiently or not, the promise adjustments its state to both fulfilled or rejected respectively. For the final two states, programmers can chain .then()and .catch() strategies with a promise to declare the logic of how the results of the asynchronous operate must be dealt with in numerous eventualities.
Other than that, a bunch of guarantees might be chained by utilizing mixture strategies like any(), all(), race(), and many others.
Even supposing guarantees have develop into a major enchancment over callbacks, they’re nonetheless not excellent, for a number of causes:
- Verbosity. Guarantees often require writing a variety of boilerplate code. In some circumstances, making a promise with a easy performance requires a couple of further strains of code due to its verbose syntax.
- Readability. Having a number of duties relying on one another results in nesting guarantees one inside one other. This notorious drawback is similar to the “callback hell” making code troublesome to learn and preserve. Moreover, when coping with error dealing with, it’s often laborious to comply with code logic when an error is propagated by means of a number of promise chains.
- Debugging. By checking the stack hint output, it is likely to be difficult to determine the supply of an error inside guarantees as they don’t often present clear error descriptions.
- Integration with legacy libraries. Many legacy libraries in JavaScript have been developed up to now to work with uncooked callbacks, thus not making it simply suitable with guarantees. If code is written by utilizing guarantees, then further code parts must be created to supply compatibility with previous libraries.
For probably the most half, the async / await building was added into JavaScript as artificial sugar over guarantees. Because the identify suggests, it introduces two new code key phrases:
asyncis used earlier than the operate signature and marks the operate as asynchronous which at all times returns a promise (even when a promise is just not returned explicitly as will probably be wrapped implicitly).awaitis used inside capabilities marked as async and is said within the code earlier than asynchronous operations which return a promise. If a line of code comprises theawaitkey phrase, then the next code strains contained in the async operate is not going to be executed till the returned promise is settled (both within the fulfilled or rejected state). This makes certain that if the execution logic of the next strains depends upon the results of the asynchronous operation, then they won’t be run.
– The
awaitkey phrase can be utilized a number of instances inside an async operate.– If
awaitis used inside a operate that’s not marked as async, theSyntaxErrorshall be thrown.– The returned results of a operate marked with
awaitit the resolved worth of a promise.
The async / await utilization instance is demonstrated within the snippet under.
// Async / await instance.
// The code snippet prints begin and finish phrases to the console.operate getPromise() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('finish');
},
1000);
});
}
// since this operate is marked as async, it can return a promise
async operate printInformation() {
console.log('begin');
const end result = await getPromise();
console.log(end result) // this line is not going to be executed till the promise is resolved
}
It is very important perceive that await doesn’t block the principle JavaScript thread from execution. As an alternative, it solely suspends the enclosing async operate (whereas different program code outdoors the async operate might be run).
Error dealing with
The async / await building offers a normal approach for error dealing with with strive / catch key phrases. To deal with errors, it’s essential to wrap all of the code that may doubtlessly trigger an error (together with await declarations) within the strive block and write corresponding deal with mechanisms within the catch block.
In observe, error dealing with with
strive / catchblocks is simpler and extra readable than reaching the identical in guarantees with.catch()rejection chaining.
// Error dealing with template inside an async operateasync operate functionOne() {
strive {
...
const end result = await functionTwo()
} catch (error) {
...
}
}
async / await is a superb various to guarantees. They remove the aforementioned shortcomings of guarantees: the code written with async / await is often extra readable, and maintainable and is a preferable selection for many software program engineers.
Nonetheless, it could be incorrect to disclaim the significance of guarantees in JavaScript: in some conditions, they’re a greater choice, particularly when working with capabilities returning a promise by default.
Code interchangeability
Allow us to take a look at the identical code written with async / await and guarantees. We are going to assume that our program connects to a database and in case of a longtime connection it requests knowledge about customers to additional show them within the UI.
// Instance of asynchronous requests dealt with by async / awaitasync operate functionOne() {
strive {
...
const end result = await functionTwo()
} catch (error) {
...
}
}
Each asynchronous requests might be simply wrapped by utilizing the await syntax. At every of those two steps, this system will cease code execution till the response is retrieved.
Since one thing mistaken can occur throughout asynchronous requests (damaged connection, knowledge inconsistency, and many others.), we must always wrap the entire code fragment right into a strive / catch block. If an error is caught, we show it to the console.
Now allow us to write the identical code fragment with guarantees:
// Instance of asynchronous requests dealt with by guaranteesoperate displayUsers() {
...
connectToDatabase()
.then((response) => {
...
return getData(knowledge);
})
.then((customers) => {
showUsers(customers);
...
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(`An error occurred: ${error.message}`);
...
});
}
This nested code appears to be like extra verbose and more durable to learn. As well as, we are able to discover that each await assertion was reworked right into a corresponding then() methodology and that the catch block is now positioned contained in the .catch() methodology of a promise.
Following the identical logic, each
async / awaitcode might be rewritten with guarantees. This assertion demonstrates the truth thatasync / awaitis simply artificial sugar over guarantees.
Code written with async / await might be reworked into the promise syntax the place every await declaration would correspond to a separate .then() methodology and exception dealing with could be carried out within the .catch() methodology.
On this part, we’ll take a look an actual instance of how async / await works.
We’re going to use the REST nations API which offers demographic info for a requested nation within the JSON format by the next URL tackle: https://restcountries.com/v3.1/identify/$nation.
Firstly, allow us to declare a operate that may retrieve the principle info from the JSON. We’re eager about retrieving info relating to the nation’s identify, its capital, space and inhabitants. The JSON is returned within the type of an array the place the primary object comprises all the required info. We are able to entry the aforementioned properties by accessing the thing’s keys with corresponding names.
const retrieveInformation = operate (knowledge) {
knowledge = knowledge[0]
return {
nation: knowledge["name"]["common"],
capital: knowledge["capital"][0],
space: `${knowledge["area"]} km`,
inhabitants: `{$knowledge["population"]} individuals`
};
};
Then we’ll use the fetch API to carry out HTTP requests. Fetch is an asynchronous operate which returns a promise. Since we instantly want the information returned by fetch, we should wait till the fetch finishes its job earlier than executing the next code strains. To try this, we use the await key phrase earlier than fetch.
// Fetch instance with async / awaitconst getCountryDescription = async operate (nation) {
strive {
const response = await fetch(
`https://restcountries.com/v3.1/identify/${nation}`
);
if (!response.okay) {
throw new Error(`Unhealthy HTTP standing of the request (${response.standing}).`);
}
const knowledge = await response.json();
console.log(retrieveInformation(knowledge));
} catch (error) {
console.log(
`An error occurred whereas processing the request.nError message: ${error.message}`
);
}
};
Equally, we place one other await earlier than the .json() methodology to parse the information which is used instantly after within the code. In case of a nasty response standing or incapacity to parse the information, an error is thrown which is then processed within the catch block.
For demonstration functions, allow us to additionally rewrite the code snippet by utilizing guarantees:
// Fetch instance with guaranteesconst getCountryDescription = operate (nation) {
fetch(`https://restcountries.com/v3.1/identify/${nation}`)
.then((response) => {
if (!response.okay) {
throw new Error(`Unhealthy HTTP standing of the request (${response.standing}).`);
}
return response.json();
})
.then((knowledge) => {
console.log(retrieveInformation(knowledge));
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(
`An error occurred whereas processing the request. Error message: ${error.message}`
);
});
};
Calling an both operate with a supplied nation identify will print its important info:
// The results of calling getCountryDescription("Argentina"){
nation: 'Argentina',
capital: 'Buenos Aires',
space: '27804000 km',
inhabitants: '45376763 individuals'
}
On this article, now we have coated the async / await building in JavaScript which appeared within the language in 2017. Having appeared as an enchancment over guarantees, it permits writing asynchronous code in a synchronous method eliminating nested code fragments. Its appropriate utilization mixed with guarantees ends in a strong mix making the code as clear as attainable.
Lastly, the knowledge introduced on this article about JavaScript can also be beneficial for Python as properly, which has the identical async / await building. Personally, if somebody desires to dive deeper into asynchronicity, I might suggest focusing extra on JavaScript than on Python. Being conscious of the ample instruments that exist in JavaScript for creating asynchronous purposes offers a neater understanding of the identical ideas in different programming languages.
All pictures until in any other case famous are by the writer.