As information turns into extra ample and data methods develop in complexity, stakeholders want options that reveal high quality insights. Making use of rising applied sciences to the geospatial area affords a novel alternative to create transformative person experiences and intuitive workstreams for customers and organizations to ship on their missions and duties.
On this put up, we discover how one can combine current methods with Amazon Bedrock to create new workflows to unlock efficiencies insights. This integration can profit technical, nontechnical, and management roles alike.
Introduction to geospatial information
Geospatial information is related to a place relative to Earth (latitude, longitude, altitude). Numerical and structured geospatial information codecs may be categorized as follows:
- Vector information – Geographical options, reminiscent of roads, buildings, or metropolis boundaries, represented as factors, strains, or polygons
- Raster information – Geographical info, reminiscent of satellite tv for pc imagery, temperature, or elevation maps, represented as a grid of cells
- Tabular information – Location-based information, reminiscent of descriptions and metrics (common rainfall, inhabitants, possession), represented in a desk of rows and columns
Geospatial information sources may additionally include pure language textual content components for unstructured attributes and metadata for categorizing and describing the report in query. Geospatial Data Techniques (GIS) present a option to retailer, analyze, and show geospatial info. In GIS functions, this info is often offered with a map to visualise streets, buildings, and vegetation.
LLMs and Amazon Bedrock
Giant language fashions (LLMs) are a subset of basis fashions (FMs) that may rework enter (often textual content or picture, relying on mannequin modality) into outputs (typically textual content) by way of a course of known as era. Amazon Bedrock is a complete, safe, and versatile service for constructing generative AI functions and brokers.
LLMs work in lots of generalized duties involving pure language. Some widespread LLM use instances embody:
- Summarization – Use a mannequin to summarize textual content or a doc.
- Q&A – Use a mannequin to reply questions on information or info from context supplied throughout coaching or inference utilizing Retrieval Augmented Technology (RAG).
- Reasoning – Use a mannequin to supply chain of thought reasoning to help a human with decision-making and speculation analysis.
- Knowledge era – Use a mannequin to generate artificial information for testing simulations or hypothetical situations.
- Content material era – Use a mannequin to draft a report from insights derived from an Amazon Bedrock information base or a person’s immediate.
- AI agent and gear orchestration – Use a mannequin to plan the invocation of different methods and processes. After different methods are invoked by an agent, the agent’s output can then be used as context for additional LLM era.
GIS can implement these capabilities to create worth and enhance person experiences. Advantages can embody:
- Stay decision-making – Taking real-time insights to assist rapid decision-making, reminiscent of emergency response coordination and visitors administration
- Analysis and evaluation – In-depth evaluation that people or methods can establish, reminiscent of pattern evaluation, patterns and relationships, and environmental monitoring
- Planning – Utilizing analysis and evaluation for knowledgeable long-term decision-making, reminiscent of infrastructure growth, useful resource allocation, and environmental regulation
Augmenting GIS and workflows with LLM capabilities results in easier evaluation and exploration of knowledge, discovery of recent insights, and improved decision-making. Amazon Bedrock offers a option to host and invoke fashions in addition to combine the AI fashions with surrounding infrastructure, which we elaborate on on this put up.
Combining GIS and AI by way of RAG and agentic workflows
LLMs are skilled with massive quantities of generalized info to find patterns in how language is produced. To enhance the efficiency of LLMs for particular use instances, approaches reminiscent of RAG and agentic workflows have been created. Retrieving insurance policies and common information for geospatial use instances may be achieved with RAG, whereas calculating and analyzing GIS information would require an agentic workflow. On this part, we broaden upon each RAG and agentic workflows within the context of geospatial use instances.
Retrieval Augmented Technology
With RAG, you may dynamically inject contextual info from a information base throughout mannequin invocation.
RAG dietary supplements a user-provided immediate with information sourced from a information base (assortment of paperwork). Amazon Bedrock affords managed information bases to information sources, reminiscent of Amazon Easy Storage Service (Amazon S3) and SharePoint, so you may present supplemental info, reminiscent of metropolis growth plans, intelligence experiences, or insurance policies and laws, when your AI assistant is producing a response for a person.
Information bases are perfect for unstructured paperwork with info saved in pure language. When your AI mannequin responds to a person with info sourced from RAG, it might probably present references and citations to its supply materials. The next diagram reveals how the methods join collectively.

As a result of geospatial information is usually structured and in a GIS, you may join the GIS to the LLM utilizing instruments and brokers as a substitute of data bases.
Instruments and brokers (to regulate a UI and a system)
Many LLMs, reminiscent of Anthropic’s Claude on Amazon Bedrock, make it potential to supply an outline of instruments accessible so your AI mannequin can generate textual content to invoke exterior processes. These processes may retrieve stay info, reminiscent of the present climate in a location or querying a structured information retailer, or may management exterior methods, reminiscent of beginning a workflow or including layers to a map. Some widespread geospatial performance that you simply may need to combine along with your LLM utilizing instruments embody:
- Performing mathematical calculations like the gap between coordinates, filtering datasets primarily based on numeric values, or calculating derived fields
- Deriving info from predictive evaluation fashions
- Wanting up factors of curiosity in structured information shops
- Looking out content material and metadata in unstructured information shops
- Retrieving real-time geospatial information, like visitors, instructions, or estimated time to achieve a vacation spot
- Visualizing distances, factors of curiosity, or paths
- Submitting work outputs reminiscent of analytic experiences
- Beginning workflows, like ordering provides or adjusting provide chain
Instruments are sometimes carried out in AWS Lambda capabilities. Lambda runs code with out the complexity and overhead of operating servers. It handles the infrastructure administration, enabling sooner growth, improved efficiency, enhanced safety, and cost-efficiency.
Amazon Bedrock affords the function Amazon Bedrock Brokers to simplify the orchestration and integration along with your geospatial instruments. Amazon Bedrock brokers observe directions for LLM reasoning to interrupt down a person immediate into smaller duties and carry out actions towards recognized duties from motion suppliers. The next diagram illustrates how Amazon Bedrock Brokers works.

The next diagram reveals how Amazon Bedrock Brokers can improve GIS options.

Resolution overview
The next demonstration applies the ideas we’ve mentioned to an earthquake evaluation agent for instance. This instance deploys an Amazon Bedrock agent with a information base primarily based on Amazon Redshift. The Redshift occasion has two tables. One desk is for earthquakes, which incorporates date, magnitude, latitude, and longitude. The second desk holds the counites in California, described as polygon shapes. The geospatial capabilities of Amazon Redshift can relate these datasets to reply queries like which county had the newest earthquake or which county has had probably the most earthquakes within the final 20 years. The Amazon Bedrock agent can generate these geospatially primarily based queries primarily based on pure language.
This script creates an end-to-end pipeline that performs the next steps:
- Processes geospatial information.
- Units up cloud infrastructure.
- Masses and configures the spatial database.
- Creates an AI agent for spatial evaluation.
Within the following sections, we create this agent and try it out.
Conditions
To implement this method, you will need to have an AWS account with the suitable AWS Id and Entry Administration (IAM) permissions for Amazon Bedrock, Amazon Redshift, and Amazon S3.
Moreover, full the next steps to arrange the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI):
- Verify you’ve gotten entry to the newest model of the AWS CLI.
- Check in to the AWS CLI along with your credentials.
- Be certain ./jq is put in. If not, use the next command:
Arrange error dealing with
Use the next code for the preliminary setup and error dealing with:
This code performs the next capabilities:
- Creates a timestamped log file
- Units up error trapping that captures line numbers
- Allows computerized script termination on errors
- Implements detailed logging of failures
Validate the AWS setting
Use the next code to validate the AWS setting:
This code performs the important AWS setup verification:
- Checks AWS CLI set up
- Validates AWS credentials
- Retrieves account ID for useful resource naming
Arrange Amazon Redshift and Amazon Bedrock variables
Use the next code to create Amazon Redshift and Amazon Bedrock variables:
Create IAM roles for Amazon Redshift and Amazon S3
Use the next code to arrange IAM roles for Amazon S3 and Amazon Redshift:
Put together the info and Amazon S3
Use the next code to arrange the info and Amazon S3 storage:
This code units up information storage and retrieval by way of the next steps:
- Creates a novel S3 bucket
- Downloads earthquake and county boundary information
- Prepares for information transformation
Remodel geospatial information
Use the next code to remodel the geospatial information:
This code performs the next actions to transform the geospatial information codecs:
- Transforms ESRI JSON to WKT format
- Processes county boundaries into CSV format
- Preserves spatial info for Amazon Redshift
Create a Redshift cluster
Use the next code to arrange the Redshift cluster:
This code performs the next capabilities:
- Units up a single-node cluster
- Configures networking and safety
- Waits for cluster availability
Create a database schema
Use the next code to create the database schema:
This code performs the next capabilities:
- Creates a counties desk with spatial information
- Creates an earthquakes desk
- Configures applicable information sorts
Create an Amazon Bedrock information base
Use the next code to create a information base:
This code performs the next capabilities:
- Creates an Amazon Bedrock information base
- Units up an Amazon Redshift information supply
- Allows spatial queries
Create an Amazon Bedrock agent
Use the next code to create and configure an agent:
This code performs the next capabilities:
- Creates an Amazon Bedrock agent
- Associates the agent with the information base
- Configures the AI mannequin and directions
Check the answer
Let’s observe the system habits with the next pure language person inputs within the chat window.
Instance 1: Summarization and Q&A
For this instance, we use the immediate “Summarize which zones enable for constructing of an condo.”
The LLM performs retrieval with a RAG method, then makes use of the retrieved residential code paperwork as context to reply the person’s question in pure language.

This instance demonstrates the LLM capabilities for hallucination mitigation, RAG, and summarization.
Instance 2: Generate a draft report
Subsequent, we enter the immediate “Write me a report on how varied zones and associated housing information may be utilized to plan new housing growth to satisfy excessive demand.”
The LLM retrieves related city planning code paperwork, then summarizes the data into a regular reporting format as described in its system immediate.

This instance demonstrates the LLM capabilities for immediate templates, RAG, and summarization.
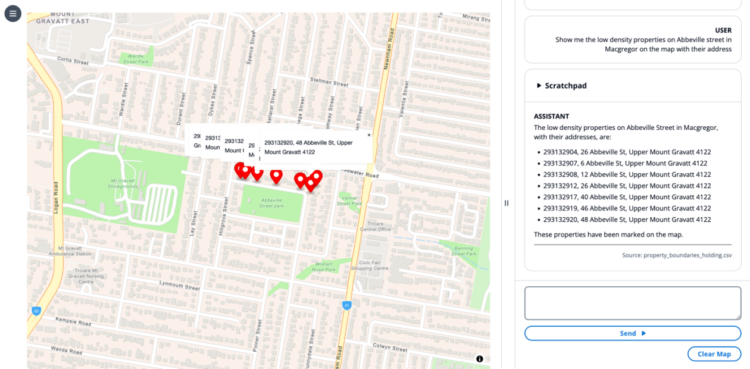
Instance 3: Present locations on the map
For this instance, we use the immediate “Present me the low density properties on Abbeville road in Macgregor on the map with their handle.”
The LLM creates a series of thought to search for which properties match the person’s question after which invokes the draw marker software on the map. The LLM offers software invocation parameters in its scratchpad, awaits the completion of those software invocations, then responds in pure language with a bulleted listing of markers positioned on the map.


This instance demonstrates the LLM capabilities for chain of thought reasoning, software use, retrieval methods utilizing brokers, and UI management.
Instance 4: Use the UI as context
For this instance, we select a marker on a map and enter the immediate “Can I construct an condo right here.”
The “right here” isn’t contextualized from dialog historical past however moderately from the state of the map view. Having a state engine that may relay info from a frontend view to the LLM enter provides a richer context.
The LLM understands the context of “right here” primarily based on the chosen marker, performs retrieval to see the land growth coverage, and responds to the person in easy pure language, “No, and right here is why…”

This instance demonstrates the LLM capabilities for UI context, chain of thought reasoning, RAG, and gear use.
Instance 5: UI context and UI management
Subsequent, we select a marker on the map and enter the immediate “draw a .25 mile circle round right here so I can visualize strolling distance.”
The LLM invokes the draw circle software to create a layer on the map centered on the chosen marker, contextualized by “right here.”

This instance demonstrates the LLM capabilities for UI context, chain of thought reasoning, software use, and UI management.
Clear up
To wash up your sources and stop AWS costs from being incurred, full the next steps:
- Delete the Amazon Bedrock information base.
- Delete the Redshift cluster.
- Delete the S3 bucket.
Conclusion
The combination of LLMs with GIS creates intuitive methods that assist customers of various technical ranges carry out advanced spatial evaluation by way of pure language interactions. Through the use of RAG and agent-based workflows, organizations can keep information accuracy whereas seamlessly connecting AI fashions to their current information bases and structured information methods. Amazon Bedrock facilitates this convergence of AI and GIS know-how by offering a sturdy platform for mannequin invocation, information retrieval, and system management, finally reworking how customers visualize, analyze, and work together with geographical information.
For additional exploration, Earth on AWS has movies and articles you may discover to grasp how AWS helps construct GIS functions on the cloud.
In regards to the Authors
 Dave Horne is a Sr. Options Architect supporting Federal System Integrators at AWS. He’s primarily based in Washington, DC, and has 15 years of expertise constructing, modernizing, and integrating methods for public sector clients. Outdoors of labor, Dave enjoys enjoying together with his children, mountaineering, and watching Penn State soccer!
Dave Horne is a Sr. Options Architect supporting Federal System Integrators at AWS. He’s primarily based in Washington, DC, and has 15 years of expertise constructing, modernizing, and integrating methods for public sector clients. Outdoors of labor, Dave enjoys enjoying together with his children, mountaineering, and watching Penn State soccer!
 Kai-Jia Yue is a options architect on the Worldwide Public Sector International Techniques Integrator Structure crew at Amazon Net Providers (AWS). She has a spotlight in information analytics and serving to buyer organizations make data-driven selections. Outdoors of labor, she loves spending time with family and friends and touring.
Kai-Jia Yue is a options architect on the Worldwide Public Sector International Techniques Integrator Structure crew at Amazon Net Providers (AWS). She has a spotlight in information analytics and serving to buyer organizations make data-driven selections. Outdoors of labor, she loves spending time with family and friends and touring.
 Brian Smitches is the Head of Companion Deployed Engineering at Windsurf specializing in how companions can carry organizational worth by way of the adoption of Agentic AI software program growth instruments like Windsurf and Devin. Brian has a background in Cloud Options Structure from his time at AWS, the place he labored within the AWS Federal Companion ecosystem. In his private time, Brian enjoys snowboarding, water sports activities, and touring with family and friends.
Brian Smitches is the Head of Companion Deployed Engineering at Windsurf specializing in how companions can carry organizational worth by way of the adoption of Agentic AI software program growth instruments like Windsurf and Devin. Brian has a background in Cloud Options Structure from his time at AWS, the place he labored within the AWS Federal Companion ecosystem. In his private time, Brian enjoys snowboarding, water sports activities, and touring with family and friends.