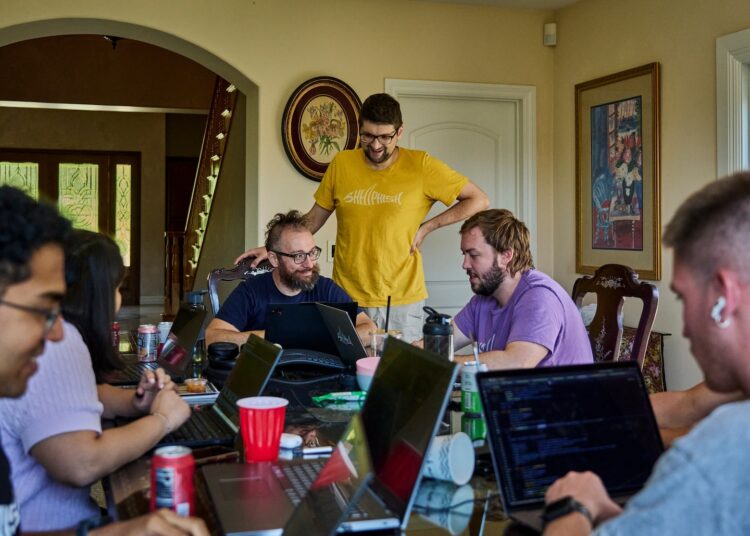
The mission of the hackathon: to jot down a program that may scan thousands and thousands of traces of open-source code, determine safety flaws and repair them, all with out human intervention. Success would imply successful thousands and thousands of {dollars} in a two-year contest sponsored by DARPA, the Protection Superior Analysis Initiatives Company.
The competition is without doubt one of the clearest indicators thus far that the federal government sees flaws in open-source software program as one of many nation’s greatest safety dangers, and considers synthetic intelligence very important to addressing it.
Free open-source applications, such because the Linux working system, assist run every little thing from web sites to energy stations. The code isn’t inherently worse than what’s in proprietary applications from firms like Microsoft and Oracle, however there aren’t sufficient expert engineers tasked with testing it.
In consequence, poorly maintained free code has been on the root of a number of the most costly cybersecurity breaches of all time, together with the 2017 Equifax catastrophe that uncovered the non-public data of half of all People. The incident, which led to the largest-ever knowledge breach settlement, price the corporate greater than $1 billion in enhancements and penalties.
If individuals can’t sustain with all of the code being woven into each industrial sector, DARPA hopes machines can.
“The aim is having an end-to-end ‘cyber reasoning system’ that leverages massive language fashions to search out vulnerabilities, show that they’re vulnerabilities, and patch them,” defined one of many advising professors, Arizona State’s Yan Shoshitaishvili.
To get there, the staff is grappling with the usually grim actuality behind lofty AI aspirations. The scholars are doing issues like imposing “sanity checks” to catch hallucinations, verifying that patches truly clear up the problems they’re imagined to, and having two AI techniques debate one another over the very best fixes — with a 3rd AI deciding the winner.
“AI is a like a 3-year-old with infinite data,” mentioned UC-Santa Barbara graduate scholar and staff co-captain Lukas Dresel. “It’s a must to give it actionable suggestions.”
Staff Shellphish is one among about 40 contestants in a contest referred to as AIxCC, for synthetic intelligence cyber problem, and run by DARPA, the Pentagon analysis arm charged with creating secret weapons and defending in opposition to them.
“We need to redefine how we safe extensively used, vital codebases, due to how ubiquitous open-source is throughout the vital infrastructure sectors,” mentioned Andrew Carney, DARPA venture supervisor for the competition.
Although DARPA helped start the web to outlive communication failures, it has turn out to be painfully apparent that the web additionally launched huge weaknesses.
With no built-in safety, the huge interconnections permit anybody or something to start out from anyplace and search for methods into machines that energy the trendy world. As soon as inside, customers can pose as workers or system directors, steal nationwide or commerce secrets and techniques, and shut the place down or maintain it up for ransom.
Hackers are claiming extra victims than ever: The variety of knowledge breaches reported to the FBI-run U.S. Web Crime Grievance Heart tripled between 2021 and 2023. Authorities brokers burrow into rival nations’ energy and water crops. Crime gangs engorged by illicit revenue assume nothing of knocking out hospitals and sending determined sufferers elsewhere.
Open-source software program, whether or not written by college students or farseeing geniuses, is nearly as ubiquitous because the web itself, by some estimates nestling inside 90% of business software program.
Like all software program, it has bugs, a few of which may be exploited to grab management of a machine.
Some massive open-source initiatives are run by near-Wikipedia-size armies of volunteers and are typically in good condition. Some have maintainers who’re given grants by huge company customers that flip it right into a job.
After which there may be every little thing else, together with applications written as homework assignments by authors who barely bear in mind them.
“Open supply has all the time been ‘Use at your personal danger,’” mentioned Brian Behlendorf, who began the Open Supply Safety Basis after many years of sustaining a pioneering free server software program, Apache, and different initiatives on the Apache Software program Basis.
“It’s not free as in speech, and even free as in beer,” he mentioned. “It’s free as in pet, and it wants care and feeding.”
The dangers have been underscored not too long ago by two very totally different incidents.
The primary was a vulnerability in a small program for protecting monitor of system exercise, referred to as Log4j, utilized by hundreds of software program builders and put in on thousands and thousands of machines.
In 2013, a person proposed including some code to Log4j, and the small Apache Basis staff sustaining Log4j accepted it. In November 2021, a Chinese language engineer noticed that the added part contained an enormous design flaw that may permit system takeovers, and he flagged the problem to the Apache group.
Whereas Apache was engaged on a patch to repair the issue, an unidentified researcher found the pending modifications and developed a malicious software to seize management of computer systems working Log4j. Apache rushed out the patch, setting off a race between hundreds of defenders and people attempting to use the flaw earlier than it was mounted.
Many Log4j situations have nonetheless not been mounted. On Thursday, the Nationwide Safety Company and others warned that North Korean spies had been nonetheless breaking into U.S. internet servers working outdated variations.
The White Home’s Cyber Security Evaluation Board concluded that solely higher coding and thorough audits may have stopped the Log4j flaw’s distribution, and that open-source efforts like Apache’s “would wish sustained monetary help and experience.”
The Division of Homeland Safety’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA) has responded with small grants to start-ups and has been pushing firms to declare what’s inside their software program. However these are slow-moving initiatives.
The newest reminder of the vulnerability got here in March. That’s when a Microsoft engineer traced a slight improve in processor use to open-source instruments for Linux that had simply been up to date. He discovered {that a} again door for spying had been inserted by the instruments’ official maintainer, and blew the whistle in time to cease it from transport in the most well-liked variations of Linux.
In a nightmare state of affairs for safety professionals, the nameless maintainer had received management of the venture after contributing for years, aided by secret allies who lobbied the earlier supervisor to cede management.
As open-source safety was rising to turn out to be a high precedence for CISA and the nationwide safety institution, OpenAI and Microsoft loosed ChatGPT and generative synthetic intelligence on the world.
By democratizing programming, the brand new instruments allowed non-coders to create software program. AI additionally aided current programmers, together with legal hackers who may extra rapidly incorporate methods to benefit from vulnerabilities and ship extra convincing lures, equivalent to emails that appeared to come back from common contacts with shared pursuits.
AI can be boosting defensive endeavors, equivalent to analyzing reams of logs for uncommon habits and summarizing safety incidents. It may additionally flag safety missteps in applications as they’re written.
However determining the place the holes in open-source applications are earlier than attackers discover them is a holy grail for DARPA and the contestants of AIxxCC.
DARPA ran a cyber problem on the 2016 Def Con hacker conference, the place applications competed in a “seize the flag” contest to hack into each other in a man-made atmosphere.
On this yr’s contest, the groups use their AI-enhanced applications to digest and enhance thousands and thousands of traces of actual code.
Shellphish is one among seven groups that wrote papers outlining their strategy nicely sufficient to get $1 million in funding for the steps that may climax on the semifinals in August at Def Con, which attracted 40 entries. The winner will get one other $2 million in 2025.
A few of Shellphish’s first million {dollars} went for the Airbnb-listed dwelling in Brea, which housed hackers for 3 weeks in June and one other two in July. Extra went for an enormous testing atmosphere that used 5,000 central processing unit cores.
Shellphish isn’t any random group of hackers. Although strongly related to two public universities with altering populations, the staff has been round for 20 years, and its founders are nonetheless concerned.
Italian native Giovanni Vigna was instructing pc safety at UC-Santa Barbara, together with strategies for attacking and defending, when he based a capture-the-flag staff in 2003 to get college students extra and stretch their capabilities. It received the Def Con competitors in 2005 and hosted the competition later for a four-year stretch.
As his college students graduated and unfold to Arizona and elsewhere, some stayed concerned, or acquired their very own college students into it.
Shellphish competed within the authentic 2016 Cyber Grand Problem, however acquired knocked out earlier than the finals.
“We had all these cool instruments however ran out of time to combine them,” Shoshitaishvili recalled. “So ‘Don’t get nerd-sniped’ was my No. 1 piece of recommendation.” (Nerd-sniping refers to distracting somebody technical with an fascinating drawback.)
Core to the trouble are instruments recognized in safety as “fuzzers.” These hearth all method of information at a program to see the way it handles the sudden.
Even souped-up fuzzers are unlikely to search out essentially the most obscure flaws or deliberate again doorways, the staff members admit. At its finest, Shellphish’s grasp program and the others will be capable to discover numerous low-hanging fruit, rapidly, and eliminate it earlier than malicious hackers can exploit them.
“AI will be capable to clear up issues that take people months,” Dresel mentioned.
Below the phrases of the DARPA contest, all finalists should launch their applications as open supply, in order that software program distributors and shoppers will be capable to run them.
Yan in contrast the anticipated advance to safety milestones like pressured software program updates and browser “sandboxes” that preserve internet applications from escaping the browser and executing elsewhere on a person’s system.
AI received’t be capable to make all software program secure, he mentioned. However it’ll give the people extra time to strive.
After a last, near-sleepless evening of debugging and panicked last-minute fixes, Shellphish submitted its program on the 9 a.m. deadline. In a number of weeks, on the subsequent Def Con in Las Vegas, they’ll discover out in the event that they’re finalists. Win or lose, their AI-aided code will likely be out there for others to construct on, bettering safety for everybody.