Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings processes textual content, paperwork, photos, video, and audio via a single mannequin structure. Accessible via Amazon Bedrock, the mannequin converts completely different enter modalities into numerical embeddings inside the identical vector house, supporting direct similarity calculations no matter content material sort. We developed this unified mannequin to cut back the necessity for separate embedding fashions, which complicate architectures, are troublesome to take care of and function, and additional restrict use instances to a one-dimensional method.
On this submit, we discover how Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings addresses the challenges of crossmodal search via a sensible ecommerce use case. We look at the technical limitations of conventional approaches and reveal how Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings permits retrieval throughout textual content, photos, and different modalities. You learn to implement a crossmodal search system by producing embeddings, dealing with queries, and measuring efficiency. We offer working code examples and share the way to add these capabilities to your functions.
The search downside
Conventional approaches contain keyword-based search, textual content embeddings-based pure language search, or hybrid search and may’t course of visible queries successfully, creating a spot between person intent and retrieval capabilities. Typical search architectures separate visible and textual processing, dropping context within the course of. Textual content queries execute towards product descriptions utilizing key phrase matching or textual content embeddings. Picture queries, when supported, function via a number of laptop imaginative and prescient pipelines with restricted integration to textual content material. This separation complicates system structure and weaken the person expertise. A number of embedding fashions require separate upkeep and optimization cycles, whereas crossmodal queries can’t be processed natively inside a single system. Visible and textual similarity scores function in several mathematical areas, making it troublesome to rank outcomes constantly throughout content material sorts. This separation requires complicated mapping that may’t all the time be achieved, so embedding methods are stored individually, creating knowledge silos within the course of and limiting performance. Complicated product content material additional complicates it, as a result of product pages mix photos, descriptions, specs, and typically video demonstrations.
Crossmodal embeddings
Crossmodal embeddings map textual content, photos, audio, and video right into a shared vector house the place semantically comparable content material clusters collectively. For instance, when processing a textual content question purple summer season gown and a picture of a purple gown, each inputs generate vectors shut collectively within the embedding house, reflecting their semantic similarity and unlocking crossmodal retrieval.
Through the use of crossmodal embeddings, you may search throughout completely different content material sorts with out sustaining separate methods for every modality, fixing the issue of segmented multimodal methods the place organizations handle a number of embedding fashions which can be practically not possible to combine successfully as a result of embeddings from completely different modalities are incompatible. A single mannequin structure helps guarantee that you’ve got constant embedding technology throughout all content material sorts whereas associated content material, similar to product photos, movies, and their descriptions, generates comparable embeddings due to joint coaching targets. Purposes can generate embeddings for all content material sorts utilizing similar API endpoints and vector dimensions, lowering system complexity.
Use case: Ecommerce search
Take into account a buyer who sees a shirt on TV and needs to search out comparable gadgets for buy. They will {photograph} the merchandise with their cellphone or attempt to describe what they noticed in textual content and use this to seek for a product. Conventional search handles textual content queries that reference metadata fairly nicely however can’t execute when prospects wish to use photos for search or describe visible attributes of an merchandise. This TV-to-cart procuring expertise reveals how visible and textual content search work collectively. The shopper uploads a photograph, and the system matches it towards product catalogs with each photos and descriptions. The crossmodal ecommerce workflow is proven within the following determine.

How Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings helps
Amazon Nova handles several types of search queries via the identical mannequin, which creates each new search capabilities and technical benefits. Whether or not you add photos, enter descriptions utilizing textual content, or mix each, the method works the identical approach.
Crossmodal search capabilities
As beforehand acknowledged, Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings processes all supported modalities via a unified mannequin structure. Enter content material will be textual content, photos, paperwork, video, or audio after which it generates embeddings in the identical vector house. This helps direct similarity calculations between completely different content material sorts with out further transformation layers. When prospects add photos, the system converts them into embeddings and searches towards the product catalog utilizing cosine similarity. You get merchandise with comparable visible traits, no matter how they’re described in textual content. Textual content queries work the identical approach—prospects can describe what they need and discover visually comparable merchandise, even when the product descriptions use completely different phrases. If the shopper uploads a picture with a textual content description, the system processes each inputs via the identical embedding mannequin for unified similarity scoring. The system additionally extracts product attributes from photos mechanically via automated product tagging, supporting semantic tag technology that goes past guide categorization.
Technical benefits
The unified structure has a number of advantages over separate textual content and picture embeddings. The only-model design and shared semantic house unlocks new use instances that aren’t attainable by managing a number of embedding methods. Purposes generate embeddings for all content material sorts utilizing the identical API endpoints and vector dimensions. A single mannequin handles all 5 modalities, so associated content material, similar to product photos and their descriptions, produce comparable embeddings. You possibly can calculate distances between any mixture of textual content, photos, audio, and video to measure how comparable they’re.
The Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings mannequin makes use of Matryoshka illustration studying, supporting a number of embedding dimensions: 3072, 1024, 384, and 256. Matryoshka embedding studying shops an important data within the first dimensions and fewer important particulars in later dimensions. You possibly can truncate from the top (proven within the following determine) to cut back cupboard space whereas sustaining accuracy on your particular use case.

Structure
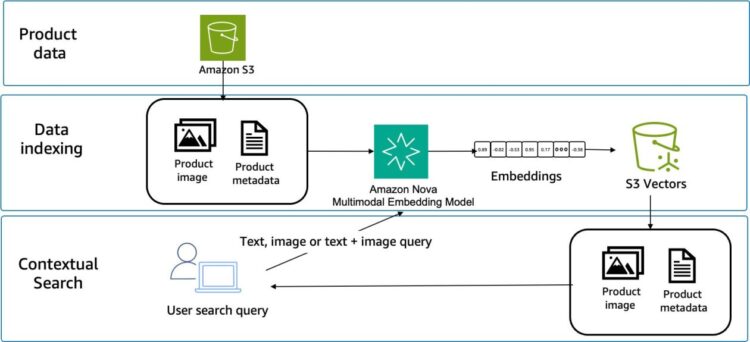
Three predominant elements are required to construct this method: embedding technology, vector storage, and similarity search. Product catalogs bear preprocessing to generate embeddings for all content material sorts. Question processing converts person inputs into embeddings utilizing the identical mannequin. Similarity search compares question embeddings towards saved product embeddings, as proven within the following determine.

Vector storage methods should help the chosen embedding dimensions and supply environment friendly similarity search operations. Choices embody purpose-built vector databases, conventional databases with vector extensions, or cloud-centered vector providers similar to Amazon S3 Vectors, a function of Amazon S3 that gives native help for storing and querying vector embeddings immediately inside S3.
Conditions
To make use of the function successfully, there are some key elements required for this implementation. An AWS account with Amazon Bedrock entry permissions for the Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings mannequin. Extra providers required embody S3 Vectors. You possibly can observe alongside within the pocket book accessible in our Amazon Nova samples repository.
Implementation
Within the following sections, we skip the preliminary knowledge obtain and extraction steps, however the end-to-end method is accessible so that you can observe alongside on this pocket book. The omitted steps embody downloading the Amazon Berkeley Objects (ABO) dataset archives, which embody product metadata, catalog photos, and 3D fashions. These archives require extraction and preprocessing to parse roughly 398,212 photos and 9,232 product listings from compressed JSON and tar information. After being extracted, the information requires metadata alignment between product descriptions and their corresponding visible property. We start this stroll via after these preliminary steps are full, specializing in the core workflow: organising S3 Vectors, producing embeddings with Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings, storing vectors at scale, and implementing crossmodal retrieval. Let’s get began.
S3 Vector bucket and index creation:
Create the vector storage infrastructure for embeddings. S3 Vectors is a managed service for storing and querying high-dimensional vectors at scale. The bucket acts as a container on your vector knowledge, whereas the index defines the construction and search traits. We configure the index with cosine distance metric, which measures similarity primarily based on vector path relatively than magnitude, making it ideally suited for normalized embeddings from fashions supplied by providers similar to Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings.
Product catalog preprocessing:
Right here we generate embeddings. Each product photos and textual descriptions require embedding technology and storage with acceptable metadata for retrieval. The Amazon Nova Embeddings API processes every modality independently, changing textual content descriptions and product photos into 1024-dimensional vectors. These vectors stay in a unified semantic house, which suggests a textual content embedding and a picture embedding of the identical product shall be geometrically shut to one another.
We use the next code to generate the embeddings and add the information to our vector retailer.
Question processing:
This code handles buyer enter via the API. Textual content queries, picture uploads, or mixtures convert into the identical vector format used on your product catalog. For multimodal queries that mix textual content and picture, we apply imply fusion to create a single question vector that captures data from each modalities. The question processing logic handles three distinct enter sorts and prepares the suitable embedding illustration for similarity search towards the S3 Vectors index.
Vector similarity search:
Subsequent, we add crossmodal retrieval utilizing the S3 Vectors question API. The system finds the closest embedding match to the question, no matter whether or not it was textual content or a picture. We use cosine similarity as the space metric, which measures the angle between vectors relatively than their absolute distance. This method works nicely for normalized embeddings and is useful resource environment friendly, making it appropriate for big catalogs when paired with approximate nearest neighbor algorithms. S3 Vectors handles the indexing and search infrastructure, so you may give attention to the appliance logic whereas the service manages scalability and efficiency optimization.
End result rating:
The similarity scores computed by S3 Vectors present the rating mechanism. Cosine similarity between question and catalog embeddings determines end result order, with greater scores indicating higher matches. In manufacturing methods, you’d usually gather click-through knowledge and relevance judgments to validate that the rating correlates with precise person conduct. S3 Vectors returns distance values which we convert to similarity scores (1 – distance) for intuitive interpretation the place greater values point out nearer matches.
Conclusion
Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings solves the core downside of crossmodal search by utilizing one mannequin as a substitute of managing separate methods. You need to use Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings to construct search that works whether or not prospects add photos, enter descriptions as textual content, or mix each approaches.
The implementation is simple utilizing Amazon Bedrock APIs, and the Matryoshka embedding dimensions allow you to optimize on your particular accuracy and price necessities. Should you’re constructing ecommerce search, content material discovery, or an utility the place customers work together with a number of content material sorts, this unified method reduces each improvement complexity and operational overhead.
Matryoshka illustration studying maintains embedding high quality throughout completely different dimensions [2]. Efficiency degradation follows predictable patterns, permitting functions to optimize for particular use instances.
Subsequent steps
Amazon Nova Multimodal Embeddings is accessible in Amazon Bedrock. See Utilizing Nova Embeddings for API references, code examples, and integration patterns for frequent architectures.
The AWS samples repository accommodates implementation examples for multimodal embeddings.
Stroll via this particular ecommerce instance pocket book right here
Concerning the authors
 Tony Santiago is a Worldwide Companion Options Architect at AWS, devoted to scaling generative AI adoption throughout International Techniques Integrators. He makes a speciality of answer constructing, technical go-to-market alignment, and functionality improvement—enabling tens of 1000’s of builders at GSI companions to ship AI-powered options for his or her prospects. Drawing on greater than 20 years of worldwide expertise expertise and a decade with AWS, Tony champions sensible applied sciences that drive measurable enterprise outcomes. Exterior of labor, he’s captivated with studying new issues and spending time with household.
Tony Santiago is a Worldwide Companion Options Architect at AWS, devoted to scaling generative AI adoption throughout International Techniques Integrators. He makes a speciality of answer constructing, technical go-to-market alignment, and functionality improvement—enabling tens of 1000’s of builders at GSI companions to ship AI-powered options for his or her prospects. Drawing on greater than 20 years of worldwide expertise expertise and a decade with AWS, Tony champions sensible applied sciences that drive measurable enterprise outcomes. Exterior of labor, he’s captivated with studying new issues and spending time with household.
 Adewale Akinfaderin is a Sr. Knowledge Scientist–Generative AI, Amazon Bedrock, the place he contributes to leading edge improvements in foundational fashions and generative AI functions at AWS. His experience is in reproducible and end-to-end AI/ML strategies, sensible implementations, and serving to international prospects formulate and develop scalable options to interdisciplinary issues. He has two graduate levels in physics and a doctorate in engineering.
Adewale Akinfaderin is a Sr. Knowledge Scientist–Generative AI, Amazon Bedrock, the place he contributes to leading edge improvements in foundational fashions and generative AI functions at AWS. His experience is in reproducible and end-to-end AI/ML strategies, sensible implementations, and serving to international prospects formulate and develop scalable options to interdisciplinary issues. He has two graduate levels in physics and a doctorate in engineering.
 Sharon Li is a options architect at AWS, primarily based within the Boston, MA space. She works with enterprise prospects, serving to them resolve troublesome issues and construct on AWS. Exterior of labor, she likes to spend time together with her household and discover native eating places.
Sharon Li is a options architect at AWS, primarily based within the Boston, MA space. She works with enterprise prospects, serving to them resolve troublesome issues and construct on AWS. Exterior of labor, she likes to spend time together with her household and discover native eating places.
 Sundaresh R. Iyer is a Companion Options Architect at Amazon Net Companies (AWS), the place he works carefully with channel companions and system integrators to design, scale, and operationalize generative AI and agentic architectures. With over 15 years of expertise spanning product administration, developer platforms, and cloud infrastructure, he makes a speciality of machine studying and AI-powered developer tooling. Sundaresh is captivated with serving to companions transfer from experimentation to manufacturing by constructing safe, ruled, and scalable AI methods that ship measurable enterprise outcomes.
Sundaresh R. Iyer is a Companion Options Architect at Amazon Net Companies (AWS), the place he works carefully with channel companions and system integrators to design, scale, and operationalize generative AI and agentic architectures. With over 15 years of expertise spanning product administration, developer platforms, and cloud infrastructure, he makes a speciality of machine studying and AI-powered developer tooling. Sundaresh is captivated with serving to companions transfer from experimentation to manufacturing by constructing safe, ruled, and scalable AI methods that ship measurable enterprise outcomes.