As enterprises quickly undertake AI brokers to automate workflows and improve productiveness, they face a important scaling problem: managing safe entry to 1000’s of instruments throughout their group. Fashionable AI deployments now not contain a handful of brokers calling a couple of APIs—as a substitute, enterprises are constructing unified AI platforms the place lots of of brokers, client AI purposes, and automatic workflows must entry 1000’s of Mannequin Context Protocol (MCP) instruments spanning completely different groups, organizations, and enterprise models.
This improve in scale creates a basic safety and governance drawback: How do you be sure that every calling principal—whether or not it’s an AI agent, person, or utility—solely accesses the instruments they’re licensed to make use of? How do you dynamically filter instrument availability based mostly on person id, agent context, the channel by way of which entry is requested, and continuously evolving permissions? How do you shield delicate knowledge because it flows by way of multi-hop workflows from brokers to instruments to downstream APIs? And the way do you accomplish all of this with out sacrificing efficiency, creating operational bottlenecks, or forcing groups to deploy separate MCP server situations for each tenant or use case?
To deal with these challenges, we’re launching a brand new function: gateway interceptors for Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Gateway. This highly effective new functionality gives fine-grained safety, dynamic entry management, and versatile schema administration.
High quality-grained entry management for instrument entry
Enterprise clients are deploying 1000’s of MCP instruments served by way of a unified AgentCore Gateway. These clients use this single MCP gateway to entry instruments from completely different groups, organizations, client AI purposes, and AI brokers, every with their corresponding entry permissions assigned to the calling principal. The problem is securing MCP instrument entry based mostly on the calling principal’s entry permissions and contextually responding to ListTools, InvokeTool, and Search calls to AgentCore Gateway.
Instrument filtering should be based mostly on a number of dynamic components, together with agent id, person id, and execution context, the place permissions would possibly change dynamically based mostly on person context, the channel by way of which the person is accessing the brokers, workspace entry ranges, and different contextual attributes. This requires security-conscious filtering the place permission adjustments instantly have an effect on instrument availability with out caching stale permission states.
The next diagram gives an instance of person based mostly instrument filtering and units the context for a way the gateway evaluates id and context earlier than returning the allowed instruments.

Schema translation and knowledge safety between MCP and downstream APIs
Prospects face complicated challenges in managing the contract between AI brokers and downstream APIs whereas sustaining safety and adaptability. Organizations should dynamically map MCP request schemas to corresponding downstream API schemas, enabling important knowledge safety capabilities corresponding to redacting or eradicating delicate knowledge like personally identifiable info (PII) or delicate private info (SPI) that customers would possibly ship as a part of prompts to brokers. This prevents delicate knowledge leakage to downstream APIs when such info isn’t wanted for the API name.
Moreover, clients require schema translation capabilities to deal with API contract adjustments whereas retaining the MCP schema intact and decoupled from downstream implementations. This decoupling permits smoother API evolution and versioning with out breaking the AI agent and gear contracts, so backend groups can modify their API implementations, change subject names, restructure payloads, or replace authentication necessities with out forcing adjustments to the agent layer or requiring retraining of AI fashions which have realized particular instrument schemas.
Tenant isolation for multi-tenant SaaS
Organizations providing brokers as a service or instruments as a service face complicated multi-tenancy necessities. Prospects should deploy their MCP servers for all their customers whereas sustaining correct tenant isolation, requiring each tenant ID and person ID to be handed and validated. Multi-tenant MCP server architectures require completely different clients and workspaces to stay fully remoted, with instrument entry strictly managed based mostly on tenant boundaries. The problem extends to figuring out whether or not separate gateways are wanted per tenant or if a single gateway can safely deal with multi-tenant situations with correct isolation ensures.
Dynamic instrument filtering
Prospects want real-time, context-aware instrument filtering that adapts to altering permissions and person contexts. Organizations require unified MCP servers that may filter instruments in two phases: first by agent permissions and workspace context, then by semantic search—with important necessities that no caching happens for dynamically filtered instrument lists as a result of permissions would possibly change at any time.
Customized header propagation and id context administration
AI brokers are basically completely different from conventional microservices in that they’re autonomous and non-deterministic of their conduct. Not like conventional microservice-to-microservice authorization approaches that usually depend on service-to-service belief and authorization strategies, AI brokers must execute workflows on behalf of end-users and entry downstream instruments, APIs, and assets based mostly on person execution context. Nevertheless, sending the unique authorization tokens to downstream companies creates vital safety vulnerabilities, corresponding to stolen credentials, privilege escalation, and the confused deputy drawback, the place a extra privileged service is tricked into performing actions on behalf of a much less privileged attacker.
Impersonation vs. act-on-behalf approaches
Prospects face a basic safety resolution in how id context propagates by way of multi-hop workflows (agent to agent to instrument to API): utilizing an impersonation method or an act-on-behalf method.
With an impersonation method, the unique person’s JWT token is handed unchanged by way of every hop within the name chain. Though easier to implement, this method creates vital safety dangers. We don’t suggest this method because of the following dangers:
- Downstream companies obtain tokens with broader privileges than vital
- Elevated threat of privilege escalation if any element is compromised
- Token scope can’t be restricted to particular downstream targets
- Weak to confused deputy assaults, the place compromised companies can abuse overly privileged tokens
In an act-on-behalf method, every hop within the workflow receives a separate, scoped token particularly issued for that downstream goal, and JWT is used for propagating the execution context all through. This method is the really helpful method as a result of it gives the next advantages:
- Precept of least privilege – Every service receives solely the permissions it must entry particular downstream APIs
- Lowered blast radius – Compromised tokens have restricted scope and might’t be reused elsewhere
- Higher auditability – A transparent chain of custody exhibits which service acted on behalf of the person utilizing AgentCore Observability
- Token scope limitation – Every downstream goal receives tokens or credentials scoped particularly for its APIs
- Safety boundaries – Correct isolation is enforced between completely different companies within the name chain
- Confused Deputy prevention – Restricted-scope tokens and credentials stop companies from being tricked into performing unauthorized actions
The act-on-behalf mannequin requires the gateway to extract execution context from incoming requests, generate new scoped authorization tokens for every downstream goal, and inject acceptable headers whereas sustaining the person’s id context for auditing and authorization choices—all with out exposing overly privileged credentials to downstream companies. This safe method makes positive AI brokers can execute workflows on behalf of customers whereas sustaining strict safety boundaries at each hop within the name chain.
The next diagram compares the workflows of impersonation vs. act-on-behalf approaches.

Within the impersonation method (prime), when Person A connects to the agent, the agent passes Person A’s full id token with full scopes ("order: learn, promotions:write") unchanged to each the Order instrument and Promotions instrument, which means every instrument receives extra permissions than it wants. In distinction, the act-on-behalf method (backside) exhibits the agent creating separate, scoped tokens for every instrument—the Order instrument receives solely the "order: learn" scope, the Promotions instrument receives solely the "promotions:write" scope, and every token contains an "Act: Agent" subject, which establishes a transparent chain of accountability exhibiting the agent is appearing on behalf of Person A. This demonstrates how delegation implements the precept of least privilege by limiting every downstream service to solely the particular permissions it wants, decreasing safety dangers and stopping potential token misuse.
AgentCore Gateway: Safe MCP integration for AI brokers
AgentCore Gateway transforms your current APIs and AWS Lambda capabilities into agent-compatible instruments, connects to current MCP servers, and gives seamless integration with important third-party enterprise instruments and companies (corresponding to Jira, Asana, and Zendesk). This unified entry level permits safe integration throughout your enterprise methods. With AgentCore Id, brokers can securely entry and function throughout these instruments with correct authentication and authorization utilizing OAuth requirements.
With the launch of gateway interceptors, AgentCore Gateway helps organizations implement fine-grained entry management and credential administration by way of customized Lambda capabilities at two important factors:
- Gateway request interceptor – The request interceptor Lambda perform processes incoming requests earlier than they attain their goal instruments, enabling fine-grained entry controlling based mostly on person credentials, session context, and organizational insurance policies, audit path creation, schema translation, and extra.
- Gateway response interceptor – The response interceptor Lambda perform processes outgoing responses earlier than they return to the calling agent, permitting for audit path creation, instruments filtering, schema translation, and fine-grained entry controlling the search and listing instruments.
The next diagram illustrates the request-response circulate by way of gateway interceptors.

Let’s look at the particular payload constructions that customized interceptors obtain and should return at every stage of the request-response cycle. The gateway request interceptor receives an occasion with the next construction:
Your gateway request interceptor Lambda perform should return a response with the transformedGatewayRequest subject:
After the goal service responds, the gateway response interceptor is invoked with an occasion containing the unique request and the response:
Your gateway response interceptor Lambda perform should return a response with the transformedGatewayResponse subject:
Understanding this request-response construction is important for implementing the customized interceptor logic we discover later on this put up. Gateway interceptors present important capabilities for securing and managing agentic AI workflows:
- Header administration – Cross authentication tokens, correlation IDs, and metadata by way of customized headers
- Request transformation – Modify request payloads, add context, or enrich knowledge earlier than it reaches goal companies
- Safety enhancement – Implement customized authentication, authorization, and knowledge sanitization logic
- High quality-grained entry management – Safe MCP instrument entry based mostly on the calling principal’s entry permissions and contextually responding to ListTools, InvokeTool, and Search calls to AgentCore Gateway
- Tenant isolation for multi-tenant MCP instruments – Implement tenant isolation and entry controls based mostly on calling person, agent, and tenant identities in a multi-tenant surroundings
- Observability – Add logging, metrics, and tracing info to observe agentic workflows
Gateway interceptors work with AgentCore Gateway goal sorts: together with Lambda capabilities, OpenAPI endpoints, and MCP servers.
Use circumstances with gateway interceptors
Gateway interceptors allow versatile safety and entry management patterns for agentic AI methods. This put up showcases three approaches: implementing fine-grained entry management for invoking instruments, dynamic instruments filtering based mostly on person permissions, and id propagation throughout distributed methods.
Implementing fine-grained entry management for invoking instruments
AgentCore Gateway exposes a number of backend instruments by way of a unified MCP endpoint. Customers with completely different roles require completely different instrument permissions. You may implement fine-grained entry management utilizing JWT scopes mixed with gateway interceptors to ensure customers can solely invoke licensed instruments and uncover instruments that belong to their function or workspace. High quality-grained entry management makes use of JWT scope values issued by Amazon Cognito (or one other OAuth 2 supplier). It’s also possible to implement this utilizing a YAML file or a database with mapped permissions. We comply with a easy naming conference: customers obtain both full entry to an MCP goal (for instance, mcp-target-123) or tool-level entry (for instance, mcp-target-123:getOrder). These scopes map on to instrument permissions within the scope declare as a part of the incoming OAuth token, making the authorization mannequin predictable and simple to audit.
The next diagram illustrates this workflow.

The request interceptor enforces permissions at execution time by way of the next steps:
- Extract and decode the JWT to retrieve the scope declare.
- Determine which instrument is being invoked (utilizing
instruments/name). - Block the request if the person lacks both full goal entry or tool-specific permission based mostly on the configuration file or entry coverage knowledge retailer.
- Return a structured MCP error for unauthorized invocations, stopping the backend instrument handler from executing.
The core authorization perform is deliberately minimal:
This sample permits predictable enforcement for each invocation and discovery paths (mentioned additional within the subsequent part). You may lengthen the mannequin with extra claims (for instance, tenantId and workspaceId) for multi-tenant architectures.
For operational safety, preserve interceptors deterministic, keep away from complicated branching logic, and rely completely on token claims somewhat than massive language mannequin (LLM) directions. By implementing authorization on the gateway boundary—earlier than the LLM sees or executes any instrument—you obtain sturdy isolation throughout roles, tenants, and domains with out modifying instrument implementations or MCP targets.
Dynamic instruments filtering
Brokers uncover accessible instruments by way of two major strategies: semantic search capabilities that permit pure language queries (like “discover instruments associated to order administration”) and commonplace (instruments/listing) operations that present an entire stock of accessible instruments. This discovery mechanism is key to agent performance, but it surely additionally presents vital safety concerns. With out correct filtering controls, MCP servers would return a complete listing of all accessible instruments, whatever the requesting agent’s or person’s authorization degree. This unrestricted instrument discovery creates potential safety vulnerabilities by exposing delicate capabilities to unauthorized customers or brokers.
When a goal returns a listing of instruments in response to semantic search or MCP instruments/listing requests, the gateway response interceptor can be utilized to implement fine-grained entry management. The interceptor processes the response earlier than it reaches the requesting agent, so customers can solely uncover instruments they’re licensed to entry. The workflow consists of the next steps:
- The goal validates the incoming JWT token and returns both the whole instrument listing or a filtered set based mostly on semantic search, regardless of fine-grained entry management.
- The configured response interceptor is invoked by AgentCore Gateway. The response interceptor extracts and decodes the JWT from the payload, retrieving the scope claims that outline the person’s permissions.
- For every instrument within the listing, the interceptor evaluates the person’s authorization based mostly on the JWT scopes.
- Instruments that the person isn’t licensed to entry are faraway from the listing.
- The response interceptor returns a remodeled response containing solely the licensed instruments.
The next diagrams illustrate this workflow for each instruments.


The next is a code snippet of the response interceptor Lambda handler that performs JWT token extraction, instrument listing retrieval, and permission-based filtering earlier than returning the remodeled response with licensed instruments:
The filter_tools_by_scope perform implements an authorization verify for every instrument towards the person’s allowed scopes:
The whole implementation may be discovered within the GitHub repo.
Customized headers propagation
As AI brokers work together with a number of downstream companies, sustaining person id throughout service boundaries turns into important for safety, compliance, and audit trails. When brokers invoke instruments by way of AgentCore Gateway, the unique person’s id should circulate from the agent to the gateway, and from the gateway to focus on companies. With out correct id propagation, downstream companies can’t implement user-specific authorization insurance policies, preserve correct audit logs, or implement tenant isolation. This problem intensifies in multi-tenant environments the place completely different customers share the identical agent infrastructure however require strict knowledge separation.
Gateway request interceptors extract id info from incoming request headers and context, remodel it into the format anticipated by downstream companies, and enrich requests earlier than they attain goal companies by following these steps:
- The gateway request interceptor extracts authorization headers from incoming requests and transforms them for downstream companies.
- AgentCore Gateway orchestrates the request circulate and manages interceptor execution.
- The goal invocation receives enriched requests with correctly formatted id info.
The gateway request interceptor helps organizations acquire end-to-end visibility into person actions, implement constant authorization insurance policies throughout service boundaries, and preserve compliance with knowledge sovereignty necessities.
The workflow consists of the next steps:
- The MCP consumer calls AgentCore Gateway.
- AgentCore Gateway authenticates the inbound request.
- AgentCore Gateway invokes the customized interceptor.
- The gateway request interceptor transforms the incoming request payload by including an authorization token as a parameter to ship to the downstream Lambda goal. (We don’t suggest sending the incoming JWT as-is to downstream APIs as a result of it’s insecure because of the threat of privilege escalation and stolen credentials. Nevertheless, there may be exceptions the place the agent must name the MCP server with an entry token for downstream APIs.) Alternatively, you’ll be able to take away the inbound JWT coming from the request and add a brand new JWT with a least-privileged scoped-down token for calling related downstream APIs.
- AgentCore Gateway calls the goal with the remodeled request. The goal has the authorization token handed by the interceptor Lambda perform.
- AgentCore Gateway returns the response from the goal.
The next diagram illustrates this workflow.

The next is a code snippet of the interceptor Lambda handler that performs customized header propagation:
No auth and OAuth based mostly authorization
Many enterprises want versatile authorization fashions that stability discoverability with safety. Think about a situation the place you need to permit AI brokers and purposes to find and search accessible MCP instruments with out requiring authorization, enabling seamless instrument exploration and semantic search throughout your instrument catalog. Nevertheless, relating to truly invoking these instruments, you want strict OAuth-based authorization to ensure solely licensed brokers and customers can execute instrument calls. You would possibly even want per-tool authorization insurance policies, the place some instruments require authentication whereas others stay publicly accessible, or the place completely different instruments require completely different permission ranges based mostly on the calling principal’s id and context.
AgentCore Gateway now helps this flexibility by way of the introduction of a “No Auth” authorization kind on the gateway degree for all inbound calls. When configured, this makes all targets and instruments accessible with out authentication for discovery functions. To implement OAuth authorization on the methodology degree (ListTools vs. CallTools) or implement per-tool authorization insurance policies, you need to use gateway interceptors to look at the inbound JWT, validate it towards the necessities based on RFC 6749 utilizing your authorization server’s discovery URL, and programmatically permit or deny entry to particular strategies or instrument calls. This method provides you fine-grained management: open discovery for ListTools and SearchTools requests whereas implementing strict OAuth validation for CallTools requests, and even implementing customized authorization logic that varies by instrument, person function, execution context, or different enterprise logic your group requires—all whereas retaining your MCP calls safe and compliant along with your safety insurance policies.
The next diagram illustrates this workflow.

The method begins with a ListTools name with No Auth to the AgentCore Gateway, which is configured with common no-auth for all inbound calls. With this configuration, customers can uncover accessible instruments with out authorization. Nevertheless, when the person subsequently makes a CallTool request to invoke a selected instrument, authorization is required. AgentCore Gateway invokes the customized request interceptor Lambda perform, which validates the JWT token from the authorization header and checks the person’s scopes and permissions towards the particular instrument being invoked. If licensed, the interceptor transforms and enriches the request with the required authorization context, and AgentCore Gateway forwards the remodeled request to the goal service. The goal processes the request and returns a response, which AgentCore Gateway then returns to the consumer, implementing strict OAuth-based authorization for precise instrument execution whereas sustaining open discovery for instrument itemizing.
To create a gateway configured with No Auth for inbound calls, use authorizerType as NONE, as proven within the following CreateGateway API:
Observability
Complete observability offered by AgentCore Observability is important for monitoring, debugging, and auditing AI agent workflows that work together with a number of instruments and companies by way of AgentCore Gateway. Gateway interceptors implement authorization, remodel requests, and filter knowledge earlier than downstream companies execute, making the observability layer a important safety boundary. This presents the next key advantages:
- Safety resolution visibility – Interceptors generate authoritative logs for authorization outcomes, together with permit/deny choices and the evaluated JWT scopes. This gives a transparent audit path for reviewing rejected requests, validating coverage conduct, and analyzing how authorization guidelines are enforced throughout instrument invocations.
- Request and response traceability – Interceptors seize how MCP requests and responses are modified, corresponding to header enrichment, schema translation, and delicate knowledge redaction. This delivers full traceability of payload adjustments and helps safe, compliant knowledge dealing with throughout agent workflows.
- Downstream instrument observability – Interceptors log downstream instrument conduct, together with standing codes, latency, and error responses. This creates constant visibility throughout targets, serving to groups troubleshoot failures, establish reliability points, and perceive end-to-end execution traits.
These logs additionally seize id and context attributes, serving to groups validate authorization conduct and isolate points in environments the place a number of person teams or tenants share the identical gateway. Gateway interceptors robotically combine with AgentCore Observability, offering the next options:
- Actual-time monitoring of authorization choices
- Efficiency bottleneck identification by way of period and invocation metrics
- Finish-to-end traceability throughout multi-hop agentic workflows
- Id and context attributes for validating authorization conduct in multi-tenant environments
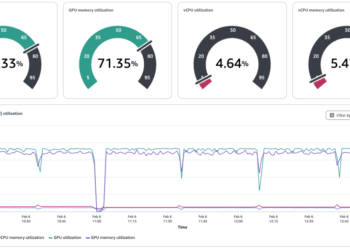
The next screenshot exhibits pattern metrics from Amazon CloudWatch log teams for a gateway interceptor.

The metrics reveal wholesome gateway interceptor efficiency with a 100% success fee, minimal latency (4.47 milliseconds common), and no throttling points, indicating the system is working inside optimum parameters.
The next screenshot exhibits pattern logs from CloudWatch for a gateway interceptor.

AgentCore Observability integration helps you monitor authorization choices in actual time, establish efficiency bottlenecks, and preserve end-to-end traceability throughout multi-hop agentic workflows.
Conclusion
AgentCore Gateway with gateway interceptors addresses the elemental safety and entry management challenges organizations face when deploying agentic AI methods at scale. The three patterns demonstrated—fine-grained entry management for instrument invocation, dynamic instrument filtering, and id propagation—present foundational constructing blocks for safe agentic architectures that bridge authentication gaps, preserve credential isolation, and implement customized safety insurance policies. By offering programmable interception factors for each requests and responses, organizations can implement fine-grained entry management with out modifying underlying instrument implementations or MCP server architectures. As organizations scale to lots of of brokers and 1000’s of instruments, gateway interceptors present the flexibleness and management wanted to take care of safety, compliance, and operational visibility throughout complicated agentic AI deployments whereas aligning with enterprise integration patterns and safety finest practices. AgentCore Gateway with gateway interceptors gives a versatile basis for implementing enterprise-grade safety controls throughout agentic AI architectures. To be taught extra about apply gateway interceptors to unravel frequent enterprise challenges, seek advice from the next code samples:
For full documentation on gateway interceptor configuration and deployment, seek advice from High quality-grained entry management for Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Gateway.
In regards to the Authors
 Dhawal Patel is a Principal Generative AI Tech lead at AWS. He has labored with organizations starting from massive enterprises to mid-sized startups on issues associated to agentic AI, deep studying, and distributed computing.
Dhawal Patel is a Principal Generative AI Tech lead at AWS. He has labored with organizations starting from massive enterprises to mid-sized startups on issues associated to agentic AI, deep studying, and distributed computing.
 Ganesh Thiyagarajan is a Senior Options Architect at AWS with over 20 years of expertise in software program structure, IT consulting, and resolution supply. He helps ISVs remodel and modernize their purposes on AWS. He’s additionally a part of the AI/ML Technical subject group, serving to clients construct and scale generative AI options.
Ganesh Thiyagarajan is a Senior Options Architect at AWS with over 20 years of expertise in software program structure, IT consulting, and resolution supply. He helps ISVs remodel and modernize their purposes on AWS. He’s additionally a part of the AI/ML Technical subject group, serving to clients construct and scale generative AI options.
 Avinash Kolluri is a Sr Options Architect at AWS. He works with Amazon and its subsidiaries to design and implement cloud options that speed up innovation and operational excellence. With deep experience in AI/ML infrastructure and distributed methods, he makes a speciality of serving to clients use AWS companies for constructing foundational fashions, workflow automation, and generative AI options.
Avinash Kolluri is a Sr Options Architect at AWS. He works with Amazon and its subsidiaries to design and implement cloud options that speed up innovation and operational excellence. With deep experience in AI/ML infrastructure and distributed methods, he makes a speciality of serving to clients use AWS companies for constructing foundational fashions, workflow automation, and generative AI options.
 Bhuvan Annamreddi is a Options Architect at AWS. He works with ISV clients to design and implement superior cloud architectures and helps them improve their merchandise by utilizing AWS companies. He’s enthusiastic about serving to clients construct scalable, safe, and progressive methods, with a powerful curiosity in generative AI and serverless structure as enablers for delivering significant enterprise worth.
Bhuvan Annamreddi is a Options Architect at AWS. He works with ISV clients to design and implement superior cloud architectures and helps them improve their merchandise by utilizing AWS companies. He’s enthusiastic about serving to clients construct scalable, safe, and progressive methods, with a powerful curiosity in generative AI and serverless structure as enablers for delivering significant enterprise worth.
 Mohammad Tahsin is a Generative AI Specialist Options Architect at AWS, the place he works with clients to design, optimize, and deploy trendy AI/ML options. He’s enthusiastic about steady studying and staying on the frontier of recent capabilities within the subject. In his free time, he enjoys gaming, digital artwork, and cooking.
Mohammad Tahsin is a Generative AI Specialist Options Architect at AWS, the place he works with clients to design, optimize, and deploy trendy AI/ML options. He’s enthusiastic about steady studying and staying on the frontier of recent capabilities within the subject. In his free time, he enjoys gaming, digital artwork, and cooking.
 Ozan Deniz works as a Software program Growth Engineer in AWS. He and his staff deal with enhancing the vendor capabilities by generative AI. When not at work, he enjoys exploring the outside.
Ozan Deniz works as a Software program Growth Engineer in AWS. He and his staff deal with enhancing the vendor capabilities by generative AI. When not at work, he enjoys exploring the outside.
 Kevin Tsao is a Software program Growth Engineer inside the AgentCore Gateway staff. He has been at Amazon for six years and has been working within the conversational AI and agentic AI house for the reason that starting of his tenure, contributing to companies corresponding to Bedrock Brokers and Amazon Lex.
Kevin Tsao is a Software program Growth Engineer inside the AgentCore Gateway staff. He has been at Amazon for six years and has been working within the conversational AI and agentic AI house for the reason that starting of his tenure, contributing to companies corresponding to Bedrock Brokers and Amazon Lex.