Within the put up Evaluating generative AI fashions with Amazon Nova LLM-as-a-Decide on Amazon SageMaker AI, we launched the Amazon Nova LLM-as-a-judge functionality, which is a specialised analysis mannequin obtainable by means of Amazon SageMaker AI that you should use to systematically measure the relative efficiency of generative AI programs.
SageMaker AI now gives a rubric-based giant language mannequin (LLM) decide powered by Amazon Nova. As a substitute of utilizing the identical normal guidelines for each activity, it mechanically creates particular analysis standards for every particular person immediate. This helps generative AI builders and machine studying (ML) engineers mechanically generate exact, scenario-specific analysis criterion for his or her LLMs and generative AI merchandise, with out manually crafting rule units for each use case.
On this put up, we discover the Amazon Nova rubric-based decide function: what a rubric-based decide is, how the decide is educated, what metrics to contemplate, and learn how to calibrate the decide. We chare pocket book code of the Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM-as-a-judge methodology to judge and evaluate the outputs of two completely different LLMs utilizing SageMaker coaching jobs.
Overview of Amazon Nova rubric-based decide
A rubric-based LLM decide makes use of a extremely succesful LLM (particularly Amazon Nova) to behave as a decide for responses generated by different AI fashions or human-generated responses. This functionality supplies pairwise comparisons between mannequin iterations, so you may make data-driven selections about mannequin enhancements with confidence. A rubric is a scoring information used to judge efficiency. Historically, to judge an AI mannequin, people manually write a guidelines of guidelines (a static rubric) that apply to each activity. For instance: “Is the reply well mannered?” or “Is the reply quick?” The problem with this strategy is that these normal guidelines don’t scale to all customers. A artistic writing immediate wants completely different grading standards than a coding immediate or a authorized abstract reasonably than one normal guidelines. The Amazon Nova powered decide creates a {custom} guidelines for various interactions. Customers ship a selected immediate to the system (for instance, “Summarize this medical doc for a affected person”). The decide analyzes that particular immediate and decides within the second what a great reply ought to appear like. It mechanically writes standards reminiscent of the next:
- Does it use easy, non-medical jargon?
- Does it seize the analysis precisely?
- Is the tone empathetic?
The decide then seems on the output generated by your LLM mannequin and grades it in opposition to these particular standards it simply created. You get a top quality rating based mostly on guidelines that had been related to that particular activity, not generic guidelines.
Instance enter
For the instance immediate or enter “do dinosaurs actually exist?”, we’ve two responses as proven within the following desk.
| Response A | Response B |
| The easy reply is: Sure, dinosaurs completely existed, however they don’t exist as we speak (besides for his or her chicken descendants). Right here’s a breakdown of what which means: 1. Dinosaurs Have been Very Actual For over 150 million years, dinosaurs had been the dominant land animals on Earth. We all know they existed as a result of we’ve an unlimited quantity of proof: Fossils: We now have discovered thousands and thousands of dinosaur fossils—bones, enamel, skulls, and claws—all around the world. These aren’t myths; they’re the precise preserved stays of those animals. Footprints: We now have found numerous fossilized trackways, that are footprints left in mud that later turned to stone. These inform us how dinosaurs walked, ran, and lived in teams. Eggs and Nests: Paleontologists have discovered fossilized dinosaur eggs and nests, displaying us how they reproduced. Even Smooth Tissues: In some extraordinarily uncommon circumstances, scientists have discovered proof of feathers, pores and skin impressions, and even chemical traces of proteins from dinosaurs. 2. However They Are Extinct (Most of Them) About 66 million years in the past, an enormous asteroid struck the Earth (in what’s now the Gulf of Mexico). This brought on a catastrophic occasion that led to the extinction of all non-avian dinosaurs—that’s, all dinosaurs apart from those that might fly. 3. Their Descendants Are All Round Us: Birds! That is essentially the most thrilling a part of the reply! Birds are literally a sort of dinosaur. Consider it this manner: The dinosaur group is big. T. rex, Triceratops, and Brachiosaurus are all well-known members. One other department of the dinosaur household tree had been small, feathered dinosaurs. One group of those feathered dinosaurs developed the flexibility to fly. They’re the direct ancestors of all fashionable birds. So, if you see a pigeon on the road or a hen in your plate, you’re looking at a residing dinosaur. In abstract:
|
Sure, dinosaurs did actually exist — however not as we speak. Dinosaurs had been a various group of reptiles that lived on Earth thousands and thousands of years in the past, primarily in the course of the Mesozoic Period, which spanned from about 252 million years in the past to 66 million years in the past. Fossil proof — together with bones, footprints, eggs, and even pores and skin impressions — confirms that dinosaurs as soon as roamed the planet. Scientists have recognized tons of of dinosaur species, starting from the large Tyrannosaurus rex and long-necked Brachiosaurus to smaller, agile predators like Velociraptor. Most non-avian dinosaurs went extinct round 66 million years in the past, seemingly due to an enormous asteroid impression mixed with volcanic exercise and local weather change. Nevertheless, one group of dinosaurs survived: the ancestors of recent birds. So in a scientific sense, birds live dinosaurs, making them the closest residing family to extinct dinosaurs like T. rex and Triceratops. So whilst you received’t see a Stegosaurus strolling round as we speak, the legacy of dinosaurs lives on — particularly each time you see a sparrow or eagle fly by. |
Instance output
Out of the 2 responses, the rubric-based decide prefers Response A and in addition supplies a justification of why it prefers response A over response B, as proven within the following screenshot.

The analysis is tailor-made to the precise intent of the person’s immediate (coding vs. writing vs. summarizing). Generative AI builders, information scientists, and ML engineers don’t need to spend tons of of hours manually writing analysis guidelines for each potential situation. You may consider hundreds of several types of prompts immediately, attaining prime quality throughout various use circumstances.
Enterprise implementation examples
The Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM decide addresses essential analysis challenges throughout completely different situations:
- Mannequin growth and checkpoint choice – Growth groups combine the Amazon Nova rubric-based decide analysis into coaching pipelines to mechanically consider checkpoints. Per-criterion scores reveal which capabilities strengthened or regressed throughout iterations, enabling data-driven selections about hyperparameter changes and information curation.
- Coaching information high quality management – Groups use the Amazon Nova rubric-based decide analysis to filter supervised fine-tuning datasets by producing point-wise scores on relevance standards, figuring out low-quality examples. For desire datasets, calculated margins between response pairs allow curriculum studying methods that filter overwhelmingly one-sided examples offering restricted studying indicators.
- Automated deep dive and root trigger evaluation – Organizations deploying generative AI at scale can use the Amazon Nova rubric-based decide analysis for systematic evaluation throughout hundreds of mannequin outputs with out guide evaluate. When fashions exhibit high quality points, builders can study which particular standards drive desire judgments, figuring out systematic weaknesses that inform focused enhancements as a substitute of broad retraining efforts.
How dynamic rubric technology works
The Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM decide takes as enter a triplet:
A rubric is a set of weighted standards used to judge the 2 responses. The rubric-based LLM decide is educated to generate standards with weights that sum to 1. Every criterion within the rubric has a short_name, description, and weight. The decide’s determination features a rating for every response on every criterion within the rubric together with justifications for the scores.
The Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM decide employs an analysis methodology the place every judgment is supported by dynamically generated, prompt-specific standards. When the decide receives an analysis request containing a immediate and candidate responses, it analyzes the immediate to know the immediate context, and generates standards based mostly on that context. This dynamic technology course of makes positive evaluations are grounded in standards straight relevant to the duty at hand, offering clear and interpretable assessments.
For every analysis, the decide produces structured YAML output containing the generated standards with their definitions, per-criterion scores on a 1–5 scale, and detailed justifications explaining every rating. The ultimate output contains one in every of 4 desire labels: [[A>B]], [[B>A]], [[A=B]], or [[A=B (bothbad)]. Every criterion rating is accompanied by a justification that grounds the evaluation in observable traits of the responses, enabling deep-dive evaluation and debugging of mannequin habits.
Evaluating rubric-based Amazon Nova LLM-as-a-judge to earlier variations
The rubric-based decide differs from earlier variations in the way it presents analysis outcomes and what info it supplies.
The earlier model of the Amazon Nova LLM-as-a-judge mannequin returned easy desire labels ([[A>B]] or [[B>A]]). The rubric-based model generates a structured YAML output that consists of the next:
- A prompt-specific rubric for assessing the responses organized as a set of standards with related per-criterion significance weights (weights sum as much as 1)
- Temporary pure language descriptions of every standards
- Likert rating (on 1–5 scale) or binary (true/false) determination for every criterion for each candidate response within the enter
- Justification for every criterion rating for each candidate response
- Total desire judgement: one in every of A>B, B>A, A=B, or A=B (each unhealthy)
The brand new detailed output format facilitates a broad vary of nuanced use circumstances. For instance, particular standards inside rubrics enable for pointed comparisons of responses. A succinct response may be extra appropriate for sure use circumstances, whereas a complete response may be wanted in others. Justifications and specific standards scoring helps customers discard sure standards which can be unsuitable for his or her wants and recompute the desire judgements with out rerunning the question although the LLM decide.
Metrics clarification
In our decide analysis course of, we use a number of vital metrics to function comparability factors for rating decide high quality. Ahead settlement is a metric which computes settlement with human desire with the chosen response and rejected response in a selected order, which makes positive the right label is at all times one in every of A>B or B>A for the complete dataset. As a result of positional consistency is a vital desired property of a reliable LLM decide, we consider our checkpoints on reconciled settlement—that’s, we receive two judgements with responses introduced to the decide in each potential orders (for 2 response desire judgements). We solely credit score the decide with an accurate reply if the decide agrees in each instructions and the judgement matches human desire. This quantity, by definition, will at all times be decrease than ahead settlement. Nevertheless, as a result of real-world datasets aren’t sorted, it supplies a extra correct proxy for the real-world efficiency of an LLM decide mannequin.
Weighted scores (weighted_score_A and weighted_score_B) are new metrics added to the rubric decide analysis output, which offer a view into the boldness of the judgment. A big distinction between the weighted scores signifies a powerful desire for one response over the over. These scores are calculated per pattern based mostly on the assigned scores for every criterion within the rubric. Every criterion rating is normalized to a 0–1 vary (the place scale scores 1–5 map to 0.0–1.0, and binary True/False map to 1.0/0.0), then multiplied by the criterion’s weight and summed to supply the weighted scores for every response.
The score_margin reveals the distinction between the weighted scores, with detrimental values indicating a desire in direction of response B and optimistic values indicating a desire in direction of response A. Within the closing analysis output, these metrics are reported as averages throughout all samples. Per-sample standards breakdowns, particular person scores, and justifications may be discovered within the detailed Parquet output file.
Per comparability pattern, we will get the particular standards that the brand new rubric decide mannequin used throughout to check the 2 outcomes, which seems like the next instance code:
These weighted metrics are informational and supply quantitative perception into the scoring breakdown, however the precise desire determination (A>B, B>A, or A=B) that determines the ultimate win counts relies on the decide mannequin’s general desire output.
Coaching strategy for the decide
The Amazon Nova rubric-based decide is educated with a multi-aspect reward bundle. In our coaching methodology, we optimize for a number of fascinating traits for an LLM decide utilizing an efficient reward formulation. We primarily goal the next standards:
- Choice accuracy – The decide is rewarded when it produces selections that align with gold human preferences. When it chooses one response over one other, the mannequin is rewarded.
- Positional consistency – The decide’s selections are educated to be resilient in direction of positional inconsistency points given a selected candidate response order.
- Justification high quality – The decide’s justifications for making the choice should align with the generated rubrics, scores, and closing judgement.
- Rating calibration – The weighted scores for the responses should be calibrated with the choice accuracy (excessive confidence judgements should be right extra usually than low confidence judgements).
We begin with human annotated desire information and make use of a {custom} information filtering and artificial information technology setup to acquire rubric-aligned desire justifications. We pattern from the generated artificial rubrics and developed a {custom} pipeline to coach the Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM decide to proficiently generate acceptable standards with exact granularity for constant and sturdy decision-making.
Benchmark efficiency
Testing on commonplace analysis datasets reveals enhancements, notably on duties requiring nuanced judgment, as proven within the following desk.
| Benchmark | Earlier Amazon Nova Decide | New Amazon Nova Rubric-Based mostly Decide |
| PPE | 0.61 | 0.64 |
| RMBench | 0.66 | 0.88 |
| RewardBench | 0.88 | 0.9 |
| JudgeBench | 0.51 | 0.76 |
| CodeUltraFeedback | 0.69 | 0.72 |
| MMEval | 0.8 | 0.84 |
The bigger enhancements on JudgeBench and RMBench mirror higher dealing with of advanced analysis situations.
Calibration
Throughout our coaching course of in addition to throughout postprocessing, we consider the Amazon Nova rubric-based decide’s capacity to make well-calibrated selections. To attain balanced calibration, we take a look at confidence buckets on a human annotated desire dataset. We take a look at the distinction of weighted scores for response pairs. We purpose for calibration of confidence to accuracy. Ideally, the LLM decide needs to be extra correct when making excessive confidence selections and is allowed to be much less correct when making low confidence selections. We discover that this calibration methodology leads to constant decision-making out and in of distribution datasets. We additionally take a look at the distributions of scores generated for various standards. We search for an roughly regular distribution over Likert scale scores (1–5) over the eval dataset. This two-pronged calibration checking course of helps us determine higher LLM decide checkpoints amongst a number of equally well-performing checkpoints.
Use circumstances of rubric-based judgement
The reliability of dynamically generated rubrics stems from three selections:
- The decide is educated on various, high-quality rubric-annotated desire information representing real-world use circumstances, instructing it patterns that distinguish efficient analysis standards from superficial ones.
- Our filtering mechanism throughout coaching prioritizes rubrics exhibiting fascinating properties—comprehensiveness, mutual exclusivity, acceptable specificity, and activity relevance—ensuring the mannequin learns from the very best examples.
- Our reward formulation straight incentivizes rubric high quality: standards that result in correct, position-invariant preferences with well-calibrated confidence receiving optimistic rewards, whereas these producing inconsistent judgments are penalized.
The best way to use rubrics to enhance sensible purposes
Many fashionable purposes function in reference-free environments, the place no gold-standard human solutions exist. In these circumstances, the usefulness of the rubric is paramount. On this part, we highlight situations the place rubrics generated by our decide could possibly be helpful inputs for knowledgeable decision-making. We reveal how outputs of our rubric-based decide—particularly the weighted standards, granular scores, and specific justifications—function essential management mechanisms.
Evaluating RAG programs
In Retrieval Augmented Technology (RAG), the first failure mode is hallucinations. Conventional desire judges sometimes conflate “is the response good?” with “is that this fluent?”, “is that this well-formatted?”, “does the interior logic maintain up?”, and so forth. A fluent however factually incorrect response is commonly perceived as extra credible than a disjointed one containing correct info. A factuality-focused analysis will help you select a summarization mannequin as a result of the retrieval outcomes don’t have hallucinations. Utilizing a rubric-based decide for such judgements may assist in understanding whether or not desire judgement relies on standards like fluency and formatting, or if the judgement relies on related standards reminiscent of faithfulness, context relevance, and so forth. Customers can disregard the scores of irrelevant standards and re-valuate judgements based mostly on a subset of standards they care about for his or her software.
The artistic critic
On this instance, we glance within the different route, the place creativity and originality are fascinating over faithfulness to real-world information or earlier context. Take into account a use case the place you’re utilizing an LLM to generate quick tales or scripts which can be authentic, however the person supplies a couple of examples of previous scripts to reveal the necessities. Choosing good outputs from these generations require the generated tales to be sufficiently completely different from the examples, artistic, authentic, and never borrow straight from current coaching information. The tip-user may index on standards reminiscent of originality, coherence, and engagement to optimize for desire judgements suited to this use case, when utilizing our rubric-based decide. You could possibly additional take a look at the specific justifications for standards scores for the particular kind of originality and creativity that’s fascinating.
Resolution overview
This resolution demonstrates learn how to consider generative AI fashions on SageMaker AI utilizing a rubric-based decide functionality. You can too consider human generated responses, however on this resolution, we present how one can consider responses generated by different LLMs reminiscent of Qwen fashions utilizing Amazon Nova as a rubric-based decide.
First, we put together a dataset by sampling questions from the Stanford Query Answering Dataset (SQuAD) and producing candidate responses from each Qwen2.5 1.5B Instruct and Qwen2.5 7B Instruct. Each fashions are accessed by means of SageMaker hosted Hugging Face endpoints. The responses from each fashions are saved in a JSONL file (llm_judge.jsonl) containing the immediate, response_A (from Qwen2.5 1.5B Instruct), and response_B (from Qwen2.5 7B Instruct).
Subsequent, the JSONL file is uploaded to an Amazon Easy Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket. A PyTorch Estimator then launches an analysis job utilizing the Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM-as-a-judge recipe. The decide mannequin dynamically generates analysis rubrics and standards tailor-made to every activity, then compares the 2 candidate responses in opposition to these standards. The job runs on GPU situations reminiscent of ml.g5.12xlarge and produces analysis metrics, together with per-criterion scores, justifications, comparative assessments, desire counts, and confidence measures. Outcomes are saved to Amazon S3 for evaluation.
Lastly, a visualization operate renders charts and tables, summarizing the generated rubrics, rating distributions throughout analysis dimensions, comparative efficiency between the 2 Qwen2.5 fashions, and detailed examples with justifications. Via this end-to-end strategy, you possibly can assess which mannequin performs higher, determine particular strengths and weaknesses, observe enhancements, and make data-driven selections about deploying generative fashions—all with out guide annotation.
Conditions
You will need to full the next conditions earlier than you possibly can run the pocket book:
- Make the next quota improve requests for SageMaker AI. For this use case, you have to request (on the Service Quotas console) a minimal of two g5.12xlarge situations for endpoint utilization and no less than one g5.12xlarge occasion for coaching job utilization.
- (Non-obligatory) You may create an Amazon SageMaker Studio area (confer with Use fast setup for Amazon SageMaker AI) to entry Jupyter notebooks with the previous IAM position. (You should use JupyterLab in your native setup, too.)
- Create an AWS Identification and Entry Administration (IAM) position with managed insurance policies
AmazonSageMakerFullAccess,AmazonS3FullAccess, andAmazonBedrockFullAccessto offer required entry to SageMaker AI and Amazon Bedrock to run the examples. - Earlier than continuing, ensure to grant the execution position direct
s3:PutObjectpermissions in your S3 bucket prefix as an inline coverage:
- Create an AWS Identification and Entry Administration (IAM) position with managed insurance policies
- Clone the GitHub repository with the property for this deployment. This repository consists of a pocket book that references coaching property.
- Run the pocket book
Amazon-Nova-Rubric-LLM-as-a-Decide-Sagemaker-AI.ipynbto begin utilizing the Amazon Nova LLM-as-a-judge implementation on SageMaker AI.
Configure fashions
To conduct a rubric-based Amazon Nova LLM-as-a-judge analysis, you have to generate outputs from each candidate fashions you need to evaluate. On this challenge, we deploy Qwen2.5 1.5B Instruct and Qwen2.5 7B Instruct on SageMaker to generate responses that will probably be in contrast by the Amazon Nova decide mannequin.
Each fashions are open-weight multilingual language fashions deployed on devoted SageMaker endpoints. That is achieved by utilizing the HuggingFaceModel deployment interface. To deploy the Qwen2.5 1.5B Instruct and Qwen2.5 7B Instruct fashions, we offer a handy script that accepts the mannequin title as an argument:
We now have additionally included the flexibility to check each of those deployed fashions. When you have got deployed the fashions, you possibly can transfer on to creating the analysis information for the rubric-based Amazon Nova LLM-as-a-judge.
Put together dataset
To create a practical analysis dataset for evaluating the Qwen fashions, we used SQuAD, a extensively adopted benchmark in pure language understanding distributed beneath the CC BY-SA 4.0 license. SQuAD consists of hundreds of crowd-sourced question-answer pairs overlaying a various vary of Wikipedia articles. By sampling from this dataset, we made positive that our analysis prompts mirrored high-quality, factual question-answering duties consultant of real-world purposes.
We started by loading a small subset of examples to maintain the workflow quick and reproducible. Particularly, we used the Hugging Face datasets library to obtain and cargo the primary 20 examples from the SQuAD coaching cut up:
This command retrieves a slice of the complete dataset, containing 20 entries with structured fields together with context, query, and solutions. To confirm the contents and examine an instance, we printed out a pattern query and its floor fact reply:
For the analysis set, we chosen the primary six questions from this subset:questions = [squad[i]["question"] for i in vary(6)]
Generate analysis dataset
After making ready a set of analysis questions from SQuAD, we generated outputs from each Qwen2.5 fashions and assembled them right into a structured dataset for use by the Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM-as-a-judge workflow. This dataset serves because the core enter for SageMaker AI analysis recipes.To do that, we iterated over every query immediate and invoked the technology operate for each SageMaker endpoints:
generate_response("qwen25-15b-instruct-endpoint", q)for completions from the Qwen2.5 1.5B Instruct mannequingenerate_response("qwen25-7b-instruct-endpoint", q)for completions from the Qwen2.5 7B Instruct mannequin
For every immediate, the workflow tried to generate a response from every mannequin.The next code calls two completely different variations of the Qwen 2.5 mannequin. This enables the LLM decide to later decide if the bigger mannequin supplies considerably higher accuracy or if the smaller mannequin is enough for the duty.
This workflow produced a JSON Strains file named llm_judge.jsonl. Every line accommodates a single analysis document structured as follows:
Then, we uploaded the llm_judge.jsonl to an S3 bucket:
Launch Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM-as-a-judge analysis job
After making ready the dataset and creating the analysis recipe, the ultimate step is to launch the SageMaker coaching job that performs the Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM-as-a-judge analysis. On this workflow, the coaching job acts as a completely managed, self-contained course of that masses the decide mannequin, processes the comparability dataset, applies dynamically generated rubrics, and generates complete analysis metrics in your designated Amazon S3 location. We use the PyTorch estimator class from the SageMaker Python SDK to encapsulate the configuration for the analysis run. The estimator defines the compute assets, container picture, analysis recipe, and output paths for storing outcomes:
After the estimator is configured, you provoke the analysis job utilizing the match() technique. This name submits the job to the SageMaker management aircraft, provisions the compute cluster (ml.g5.12xlarge situations), and begins processing your analysis dataset:
estimator.match(inputs={"practice": evalInput})The job will execute the rubric-based comparability, with the Amazon Nova decide mannequin dynamically producing analysis standards and scoring each Qwen2.5 mannequin outputs. Outcomes, together with per-criterion scores, justifications, and comparative assessments, are mechanically saved to your specified S3 output path for downstream evaluation and visualization.
Outcomes from Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM-as-a-judge analysis job
The next is an instance consequence for a row of the analysis. On this instance, Assistant B is the clear winner as a result of it prioritizes grounded, nuanced info over Assistant A’s suspiciously particular however unverified declare of 145 newspapers. The decide penalizes Assistant A for its lack of context, leading to considerably decrease scores for accuracy and completeness. By making use of a {custom} weight that allocates 50% of the entire rating to accuracy, the analysis calculates a weighted margin that quantifies exactly why Assistant B’s detailed, verifiable response is superior.
As within the put up Evaluating generative AI fashions with Amazon Nova LLM-as-a-Decide on Amazon SageMaker AI, to assist practitioners rapidly interpret the end result of an Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM-as-a-judge analysis, we created a comfort operate that produces a single, complete visualization summarizing key metrics, as proven within the following screenshot.

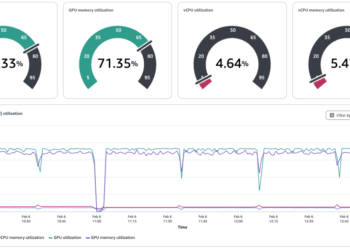
This operate, plot_nova_judge_results, makes use of Matplotlib and Seaborn to render a picture with six panels, every highlighting a distinct perspective of the analysis end result.
This operate takes the analysis metrics dictionary produced when the analysis job is full and generates the next visible parts:
- Rating distribution bar chart – Exhibits what number of occasions Mannequin A was most popular (three wins), what number of occasions Mannequin B was most popular (seven wins), what number of ties occurred, and the way usually the decide failed to supply a call (one inference error out of 11 evaluations). This supplies a direct sense of how decisive the analysis was, clearly displaying Mannequin B’s dominance with a 70% desire charge.
- Win charge with 95% confidence interval – Plots Mannequin B’s general win charge of 70% in opposition to Mannequin A, together with an error bar reflecting the boldness interval bounds of [0.400, 0.909]. A vertical reference line at 50% marks the purpose of no desire. As a result of the boldness interval doesn’t cross this line, we will conclude the result’s statistically vital, indicating significant superiority for the 7B mannequin.
- Choice pie chart – Visually shows the proportion of preferences among the many 10 legitimate judgments: 70% for Mannequin B and 30% for Mannequin A. This will help customers rapidly perceive the clear desire distribution favoring the bigger mannequin.
- A vs. B rating comparability bar chart – Compares the uncooked counts of preferences for every mannequin facet by facet (three for Mannequin A vs seven for Mannequin B). A transparent label annotates the margin of distinction, emphasizing Mannequin B’s four-win benefit. The chart additionally shows the weighted rubric-based scores: Mannequin A averaged 0.495 whereas Mannequin B averaged 0.630 throughout all analysis standards (accuracy, completeness, readability), with a mean margin of -0.135 favoring Mannequin B.
- Win charge gauge – Depicts the 70% win charge as a semicircular gauge with a needle pointing to Mannequin B’s efficiency relative to the theoretical 0–100% vary. This intuitive visualization helps nontechnical stakeholders instantly grasp that Mannequin B outperformed Mannequin A by a considerable margin based mostly on dynamically generated rubric standards tailor-made to every question-answer pair.
- Abstract statistics desk – Compiles numerical metrics right into a compact, clear desk: 11 complete evaluations, one error (9.1% error charge), 70% win charge, weighted rubric scores (0.630 for B vs 0.495 for A with -0.135 margin), and confidence intervals [0.400, 0.909]. This makes it simple to reference the precise numeric values behind the plots and perceive each the statistical rigor and rubric-based evaluation of the analysis.
As a result of the operate outputs a normal Matplotlib determine, you possibly can rapidly save the picture, show it in Jupyter notebooks, or embed it in different documentation. The visualization clearly demonstrates that Mannequin B reveals statistically vital superiority general with increased rubric-based scores throughout accuracy, completeness, and readability dimensions.
Clear up
To cease and delete the SageMaker Studio areas, comply with these clear up steps within the SageMaker Studio documentation. You will need to delete the S3 bucket and the hosted mannequin endpoint to cease incurring prices. You may delete the real-time endpoints you created utilizing the SageMaker console. For directions, see Delete Endpoints and Sources.
Conclusion
Evaluating generative AI outputs at scale requires greater than easy desire labels, it requires transparency into why one response outperforms one other. The Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM decide addresses this want by dynamically producing task-specific analysis standards, offering per-criterion scores with specific justifications, and delivering well-calibrated confidence indicators. In comparison with earlier decide implementations, the rubric-based strategy gives three key benefits: interpretability by means of structured YAML output with criterion-level breakdowns, flexibility enabling customers to reweight or filter standards for his or her particular use circumstances, and improved accuracy with vital features throughout commonplace benchmarks—together with a 49% enchancment on advanced analysis situations in JudgeBench. If you’re choosing mannequin checkpoints throughout growth, filtering coaching information for high quality, or debugging manufacturing mannequin habits at scale, the Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM-as-a-judge analysis transforms opaque desire selections into actionable insights. By exposing the reasoning behind every judgment, groups can determine systematic weaknesses, validate that evaluations align with their high quality priorities, and construct higher belief in automated analysis pipelines.
To get began with the Amazon Nova rubric-based LLM decide on SageMaker AI, confer with Rubric Based mostly Decide.
In regards to the authors
 Surya Kari is a Senior Generative AI Knowledge Scientist at AWS, specializing in creating options leveraging state-of-the-art basis fashions. He has intensive expertise working with superior language fashions together with DeepSeek-R1, the Llama household, and Qwen, specializing in their fine-tuning and optimization for particular scientific purposes. His experience extends to implementing environment friendly coaching pipelines and deployment methods utilizing AWS SageMaker, enabling the scaling of basis fashions from growth to manufacturing. He collaborates with clients to design and implement generative AI options, serving to them navigate mannequin choice, fine-tuning approaches, and deployment methods to realize optimum efficiency for his or her particular use circumstances.
Surya Kari is a Senior Generative AI Knowledge Scientist at AWS, specializing in creating options leveraging state-of-the-art basis fashions. He has intensive expertise working with superior language fashions together with DeepSeek-R1, the Llama household, and Qwen, specializing in their fine-tuning and optimization for particular scientific purposes. His experience extends to implementing environment friendly coaching pipelines and deployment methods utilizing AWS SageMaker, enabling the scaling of basis fashions from growth to manufacturing. He collaborates with clients to design and implement generative AI options, serving to them navigate mannequin choice, fine-tuning approaches, and deployment methods to realize optimum efficiency for his or her particular use circumstances.
 Joseph Moulton is a Software program Engineer on the Amazon AGI Customization group supporting the implementation of analysis and inference workflows for AWS Nova Forge. Present work focuses on creating and implementing new methods for patrons to judge their {custom} educated Nova fashions. He has been with the corporate as a software program engineer for 4 years, becoming a member of the Alexa AI Machine Studying platform group in 2022 earlier than transitioning to the Nova Forge group in 2025. In his free time he enjoys {golfing} and constructing computer systems.
Joseph Moulton is a Software program Engineer on the Amazon AGI Customization group supporting the implementation of analysis and inference workflows for AWS Nova Forge. Present work focuses on creating and implementing new methods for patrons to judge their {custom} educated Nova fashions. He has been with the corporate as a software program engineer for 4 years, becoming a member of the Alexa AI Machine Studying platform group in 2022 earlier than transitioning to the Nova Forge group in 2025. In his free time he enjoys {golfing} and constructing computer systems.
 Morteza Ziyadi is an senior science lead and supervisor at Amazon AGI, the place he leads a number of tasks on post-training recipes and (Multimodal) giant language fashions within the Amazon AGI Basis modeling group. Earlier than becoming a member of Amazon AGI, he spent 4 years at Microsoft Cloud and AI, the place he led tasks centered on creating pure language-to-code technology fashions for varied merchandise. He has additionally served as an adjunct college at Northeastern College. He earned his PhD from the College of Southern California (USC) in 2017 and has since been actively concerned as a workshop organizer, and reviewer for quite a few NLP, Laptop Imaginative and prescient and machine studying conferences.
Morteza Ziyadi is an senior science lead and supervisor at Amazon AGI, the place he leads a number of tasks on post-training recipes and (Multimodal) giant language fashions within the Amazon AGI Basis modeling group. Earlier than becoming a member of Amazon AGI, he spent 4 years at Microsoft Cloud and AI, the place he led tasks centered on creating pure language-to-code technology fashions for varied merchandise. He has additionally served as an adjunct college at Northeastern College. He earned his PhD from the College of Southern California (USC) in 2017 and has since been actively concerned as a workshop organizer, and reviewer for quite a few NLP, Laptop Imaginative and prescient and machine studying conferences.
 Rajkumar Pujari is an Utilized Scientist II on the Nova Fashions post-training group at Amazon AGI. He obtained his Ph.D. in Laptop Science from Purdue College, specializing in Machine Studying for Computational Social Science. Presently, his work focuses on post-training and reinforcement studying for Massive Language Fashions. He develops large-scale, dynamic analysis pipelines for frontier fashions and builds LLM-as-a-Decide frameworks.
Rajkumar Pujari is an Utilized Scientist II on the Nova Fashions post-training group at Amazon AGI. He obtained his Ph.D. in Laptop Science from Purdue College, specializing in Machine Studying for Computational Social Science. Presently, his work focuses on post-training and reinforcement studying for Massive Language Fashions. He develops large-scale, dynamic analysis pipelines for frontier fashions and builds LLM-as-a-Decide frameworks.
 Swastik Roy is a Senior Utilized Scientist on Amazon’s AGI Basis group, specializing in generalizability analysis and post-training of the Amazon Nova household of fashions. His experience spans fine-tuning, reinforcement studying, and analysis methodologies, the place he drives efforts to advance the robustness of foundational AI programs.
Swastik Roy is a Senior Utilized Scientist on Amazon’s AGI Basis group, specializing in generalizability analysis and post-training of the Amazon Nova household of fashions. His experience spans fine-tuning, reinforcement studying, and analysis methodologies, the place he drives efforts to advance the robustness of foundational AI programs.
 Joel Catapano is a Senior Utilized Scientist on the Amazon AGI basis modeling group. He primarily works on creating novel approaches for enhancing the LLM-as-a-Decide functionality of the Nova household of fashions.
Joel Catapano is a Senior Utilized Scientist on the Amazon AGI basis modeling group. He primarily works on creating novel approaches for enhancing the LLM-as-a-Decide functionality of the Nova household of fashions.
 Mona Mona is a Sr World Extensive Gen AI Specialist Options Architect specializing in Gen AI Options in Amazon SageMaker AI group. She was a Lead Generative AI specialist in Google earlier than becoming a member of Amazon. She is a broadcast creator of two books – Pure Language Processing with AWS AI Companies and Google Cloud Licensed Skilled Machine Studying Research Information. She has authored 20+ blogs on AI/ML and cloud expertise and a co-author on a analysis paper on CORD19 Neural Search which received an award for Finest Analysis Paper on the prestigious AAAI (Affiliation for the Development of Synthetic Intelligence) convention.
Mona Mona is a Sr World Extensive Gen AI Specialist Options Architect specializing in Gen AI Options in Amazon SageMaker AI group. She was a Lead Generative AI specialist in Google earlier than becoming a member of Amazon. She is a broadcast creator of two books – Pure Language Processing with AWS AI Companies and Google Cloud Licensed Skilled Machine Studying Research Information. She has authored 20+ blogs on AI/ML and cloud expertise and a co-author on a analysis paper on CORD19 Neural Search which received an award for Finest Analysis Paper on the prestigious AAAI (Affiliation for the Development of Synthetic Intelligence) convention.
 Pradeep Natarajan is a Senior Principal Scientist in Amazon AGI Basis modeling group engaged on post-training recipes and Multimodal giant language fashions. He has 20+ years of expertise in creating and launching a number of large-scale machine studying programs. He has a PhD in Laptop Science from College of Southern California.
Pradeep Natarajan is a Senior Principal Scientist in Amazon AGI Basis modeling group engaged on post-training recipes and Multimodal giant language fashions. He has 20+ years of expertise in creating and launching a number of large-scale machine studying programs. He has a PhD in Laptop Science from College of Southern California.