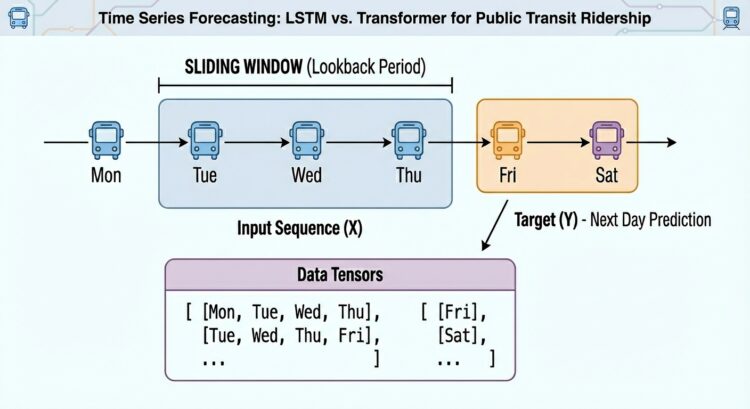
On this article, you’ll learn to construct, practice, and examine an LSTM and a transformer for next-day univariate time sequence forecasting on actual public transit knowledge.
Matters we’ll cowl embrace:
- Structuring and windowing a time sequence for supervised studying.
- Implementing compact LSTM and transformer architectures in PyTorch.
- Evaluating and evaluating fashions with MAE and RMSE on held-out knowledge.
All proper, full steam forward.
Transformer vs LSTM for Time Sequence: Which Works Higher?
Picture by Editor
Introduction
From day by day climate measurements or visitors sensor readings to inventory costs, time sequence knowledge are current practically all over the place. When these time sequence datasets grow to be more difficult, fashions with the next stage of sophistication — similar to ensemble strategies and even deep studying architectures — is usually a extra handy possibility than classical time sequence evaluation and forecasting methods.
The target of this text is to showcase how two deep studying architectures are skilled and used to deal with time sequence knowledge — lengthy brief time period reminiscence (LSTM) and the transformer. The primary focus isn’t merely leveraging the fashions, however understanding their variations when dealing with time sequence and whether or not one structure clearly outperforms the opposite. Fundamental data of Python and machine studying necessities is really useful.
Drawback Setup and Preparation
For this illustrative comparability, we’ll think about a forecasting activity on a univariate time sequence: given the temporally ordered earlier N time steps, predict the (N+1)th worth.
Specifically, we’ll use a publicly out there model of the Chicago rides dataset, which comprises day by day recordings for bus and rail passengers within the Chicago public transit community courting again to 2001.
This preliminary piece of code imports the libraries and modules wanted and masses the dataset. We are going to import pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, and PyTorch — all for the heavy lifting — together with the scikit-learn metrics that we’ll depend on for analysis.
|
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch import torch.nn as nn from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error
url = “https://knowledge.cityofchicago.org/api/views/6iiy-9s97/rows.csv?accessType=DOWNLOAD” df = pd.read_csv(url, parse_dates=[“service_date”]) print(df.head()) |
Because the dataset comprises post-COVID actual knowledge about passenger numbers — which can severely mislead the predictive energy of our fashions attributable to being very in another way distributed than pre-COVID knowledge — we’ll filter out data from January 1, 2020 onwards.
|
df_filtered = df[df[‘service_date’] <= ‘2019-12-31’]
print(“Filtered DataFrame head:”) show(df_filtered.head())
print(“nShape of the filtered DataFrame:”, df_filtered.form) df = df_filtered |
A easy plot will do the job to indicate what the filtered knowledge appears to be like like:
|
df.sort_values(“service_date”, inplace=True) ts = df.set_index(“service_date”)[“total_rides”].fillna(0)
plt.plot(ts) plt.title(“CTA Every day Whole Rides”) plt.present() |
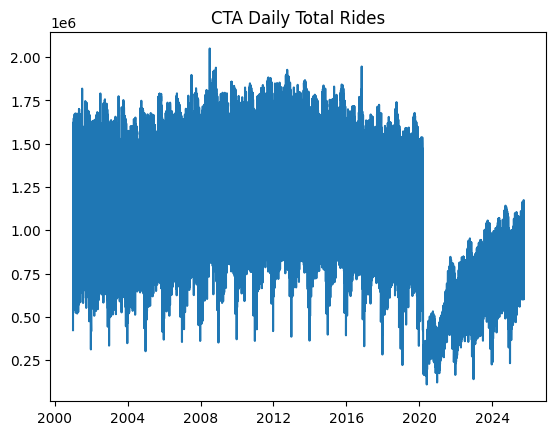
Chicago rides time sequence dataset plotted
Subsequent, we break up the time sequence knowledge into coaching and check units. Importantly, in time sequence forecasting duties — not like classification and regression — this partition can’t be accomplished at random, however in a purely sequential trend. In different phrases, all coaching cases come chronologically first, adopted by check cases. This code takes the primary 80% of the time sequence as a coaching set, and the remaining 20% for testing.
|
n = len(ts) practice = ts[:int(0.8*n)] check = ts[int(0.8*n):]
train_vals = practice.values.astype(float) test_vals = check.values.astype(float) |
Moreover, uncooked time sequence have to be transformed into labeled sequences (x, y) spanning a hard and fast time window to correctly practice neural network-based fashions upon them. For instance, if we use a time window of N=30 days, the primary occasion will span the primary 30 days of the time sequence, and the related label to foretell would be the thirty first day, and so forth. This provides the dataset an applicable labeled format for supervised studying duties with out dropping its necessary temporal that means:
|
def create_sequences(knowledge, seq_len=30): X, y = [], [] for i in vary(len(knowledge)–seq_len): X.append(knowledge[i:i+seq_len]) y.append(knowledge[i+seq_len]) return np.array(X), np.array(y)
SEQ_LEN = 30 X_train, y_train = create_sequences(train_vals, SEQ_LEN) X_test, y_test = create_sequences(test_vals, SEQ_LEN)
# Convert our formatted knowledge into PyTorch tensors X_train = torch.tensor(X_train).float().unsqueeze(–1) y_train = torch.tensor(y_train).float().unsqueeze(–1) X_test = torch.tensor(X_test).float().unsqueeze(–1) y_test = torch.tensor(y_test).float().unsqueeze(–1) |
We are actually prepared to coach, consider, and examine our LSTM and transformer fashions!
Mannequin Coaching
We are going to use the PyTorch library for the modeling stage, because it gives the mandatory courses to outline each recurrent LSTM layers and encoder-only transformer layers appropriate for predictive duties.
First up, we have now an LSTM-based RNN structure like this:
|
class LSTMModel(nn.Module): def __init__(self, hidden=32): tremendous().__init__() self.lstm = nn.LSTM(1, hidden, batch_first=True) self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden, 1)
def ahead(self, x): out, _ = self.lstm(x) return self.fc(out[:, –1])
lstm_model = LSTMModel() |
As for the encoder-only transformer for next-day time sequence forecasting, we have now:
|
class SimpleTransformer(nn.Module): def __init__(self, d_model=32, nhead=4): tremendous().__init__() self.embed = nn.Linear(1, d_model) enc_layer = nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(d_model=d_model, nhead=nhead, batch_first=True) self.transformer = nn.TransformerEncoder(enc_layer, num_layers=1) self.fc = nn.Linear(d_model, 1)
def ahead(self, x): x = self.embed(x) x = self.transformer(x) return self.fc(x[:, –1])
transformer_model = SimpleTransformer() |
Word that the final layer in each architectures follows an identical sample: its enter form is the hidden illustration dimensionality (32 in our instance), and one single neuron is used to carry out a single forecast of the next-day whole rides.
Time to coach the fashions and consider each fashions’ efficiency with the check knowledge:
|
def practice(mannequin, X, y, epochs=10): mannequin.practice() decide = torch.optim.Adam(mannequin.parameters(), lr=1e–3) loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
for epoch in vary(epochs): decide.zero_grad() out = mannequin(X) loss = loss_fn(out, y) loss.backward() decide.step() return mannequin
lstm_model = practice(lstm_model, X_train, y_train) transformer_model = practice(transformer_model, X_train, y_train) |
We are going to examine how the fashions carried out for a univariate time sequence forecasting activity utilizing two frequent metrics: imply absolute error (MAE) and root imply squared error (RMSE).
|
lstm_model.eval() transformer_model.eval()
pred_lstm = lstm_model(X_test).detach().numpy().flatten() pred_trans = transformer_model(X_test).detach().numpy().flatten() true_vals = y_test.numpy().flatten()
rmse_lstm = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(true_vals, pred_lstm)) mae_lstm = mean_absolute_error(true_vals, pred_lstm)
rmse_trans = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(true_vals, pred_trans)) mae_trans = mean_absolute_error(true_vals, pred_trans)
print(f“LSTM RMSE={rmse_lstm:.1f}, MAE={mae_lstm:.1f}”) print(f“Trans RMSE={rmse_trans:.1f}, MAE={mae_trans:.1f}”) |
Outcomes Dialogue
Listed here are the outcomes we obtained:
|
LSTM RMSE=1350000.8, MAE=1297517.9 Trans RMSE=1349997.3, MAE=1297514.1 |
The outcomes are extremely related between the 2 fashions, making it troublesome to find out whether or not one is best than the opposite (if we glance intently, the transformer performs a tiny bit higher, however the distinction is actually negligible).
Why are the outcomes so related? Univariate time sequence forecasting on knowledge that observe a fairly constant sample over time, such because the dataset we think about, can yield related outcomes throughout these fashions as a result of each have sufficient capability to resolve this drawback — though the complexity of every structure right here is deliberately minimal. I counsel you attempt the complete course of once more with out filtering the post-COVID cases, holding the identical 80/20 ratio for coaching and testing over the complete authentic dataset, and see if the distinction between the 2 fashions will increase (be at liberty to remark beneath together with your findings).
Apart from, the forecasting activity could be very short-term: we’re simply predicting the next-day worth, as a substitute of getting a extra advanced label set y that spans a subsequent time window to the one thought-about for inputs X. If we predicted values 30 days forward, the distinction between the fashions’ errors would doubtless widen, with the transformer arguably outperforming the LSTM (though this won’t at all times be the case).
Wrapping Up
This text showcased learn how to tackle a time sequence forecasting activity with two completely different deep studying architectures: LSTM and the transformer. We guided you thru the complete course of, from acquiring the info to coaching the fashions, evaluating them, evaluating, and deciphering outcomes.