Language mannequin coaching is gradual, even when your mannequin is just not very massive. It is because you want to prepare the mannequin with a big dataset and there’s a massive vocabulary. Subsequently, it wants many coaching steps for the mannequin to converge. Nonetheless, there are some strategies recognized to hurry up the coaching course of. On this article, you’ll study them. Specifically, you’ll study:
- Utilizing optimizers
- Utilizing studying charge schedulers
- Different strategies for higher convergence or diminished reminiscence consumption
Let’s get began.

The best way to Pace-Up Coaching of Language Fashions
Photograph by Emma Fabbri. Some rights reserved.
Overview
This text is split into 4 elements; they’re:
- Optimizers for Coaching Language Fashions
- Studying Price Schedulers
- Sequence Size Scheduling
- Different Strategies to Assist Coaching Deep Studying Fashions
Optimizers for Coaching Language Fashions
Adam has been the preferred optimizer for coaching deep studying fashions. In contrast to SGD and RMSProp, Adam makes use of each the primary and second second of the gradient to replace the parameters. Utilizing the second second may also help the mannequin converge sooner and extra stably, on the expense of utilizing extra reminiscence.
Nonetheless, when coaching language fashions these days, you’ll normally use AdamW, the Adam optimizer with weight decay. Weight decay is a regularization approach to stop overfitting. It normally includes including a small penalty to the loss perform. However in AdamW, the load decay is utilized on to the weights as an alternative. That is believed to be extra secure as a result of the regularization time period is decoupled from the calculated gradient. It’s also extra strong to hyperparameter tuning, because the impact of the regularization time period is utilized explicitly to the load replace.
In method, AdamW weight replace algorithm is as follows:
$$
start{aligned}
g_t &= nabla_theta L(theta_{t-1})
m_t &= beta_1 m_{t-1} + (1 – beta_1) g_t
v_t &= beta_2 v_{t-1} + (1 – beta_2) g_t^2
hat{m_t} &= m_t / (1 – beta_1^t)
hat{v_t} &= v_t / (1 – beta_2^t)
theta_t &= theta_{t-1} – alpha Large( frac{hat{m_t}}{sqrt{hat{v_t}} + epsilon} + lambda theta_{t-1} Large)
finish{aligned}
$$
The mannequin weight at step $t$ is denoted by $theta_t$. The $g_t$ is the computed gradient from the loss perform $L$, and $g_t^2$ is the elementwise sq. of the gradient. The $m_t$ and $v_t$ are the transferring common of the primary and second second of the gradient, respectively. Studying charge $alpha$, weight decay $lambda$, and transferring common decay charges $beta_1$ and $beta_2$ are hyperparameters. A small worth $epsilon$ is used to keep away from division by zero. A typical selection can be $beta_1 = 0.9$, $beta_2 = 0.999$, $epsilon = 10^{-8}$, and $lambda = 0.1$.
The important thing of AdamW is the $lambda theta_{t-1}$ time period within the gradient replace, as an alternative of within the loss perform.
AdamW is just not the one selection of optimizer. Some newer optimizers have been proposed just lately, akin to Lion, SOAP, and AdEMAMix. You may see the paper Benchmarking Optimizers for Giant Language Mannequin Pretraining for a abstract.
Studying Price Schedulers
A studying charge scheduler is used to regulate the training charge throughout coaching. Often, you would like a bigger studying charge for the early coaching steps and scale back the training charge as coaching progresses to assist the mannequin converge. You may add a warm-up interval to extend the training charge from a small worth to the height over a brief interval (normally 0.1% to 2% of whole steps), then the training charge is decreased over the remaining coaching steps.
A warm-up interval normally begins with a near-zero studying charge and will increase linearly to the height studying charge. A mannequin begins with randomized preliminary weights. Beginning with a big studying charge may cause poor convergence, particularly for giant fashions, massive batches, and adaptive optimizers.
You may see the necessity for warm-up from the equations above. Assume the mannequin is uncalibrated; the loss might fluctuate enormously between subsequent steps. Then the primary and second moments $m_t$ and $v_t$ will likely be fluctuating enormously, and the gradient replace $theta_t – theta_{t-1}$ will even be fluctuating enormously. Therefore, you would like the loss to be secure and transfer slowly in order that AdamW can construct a dependable operating common. This may be simply achieved if $alpha$ is small.
On the studying charge discount section, there are a couple of decisions:
- cosine decay: $LR = LR_{max} cdot frac12 Large(1 + cos frac{pi t}{T}Large)$
- square-root decay: $LR = LR_{max} cdot sqrt{frac{T – t}{T}}$
- linear decay: $LR = LR_{max} cdot frac{T – t}{T}$
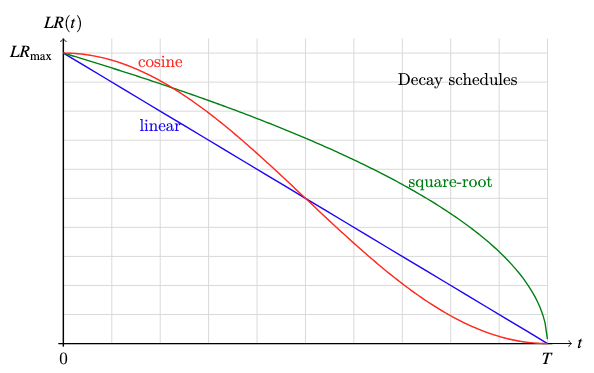
Plot of the three decay features
A big studying charge may also help the mannequin converge sooner whereas a small studying charge may also help the mannequin stabilize. Subsequently, you need the training charge to be massive initially when the mannequin continues to be uncalibrated, however small on the finish when the mannequin is near its optimum state. All decay schemes above can obtain this, however you wouldn’t need the training charge to turn out to be “too small too quickly” or “too massive too late”. Cosine decay is the preferred selection as a result of it drops the training charge extra slowly initially and stays longer at a low studying charge close to the tip, that are fascinating properties to assist the mannequin converge sooner and stabilize respectively.
n PyTorch, you could have the CosineAnnealingLR scheduler to implement cosine decay. For the warm-up interval, you want to mix with the LinearLR scheduler. Under is an instance of the coaching loop utilizing AdamW, CosineAnnealingLR, and LinearLR:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LinearLR, CosineAnnealingLR, SequentialLR
# Instance setup mannequin = torch.nn.Linear(10, 1) X, y = torch.randn(5, 10), torch.randn(5) loss_fn = nn.MSELoss() optimizer = optim.AdamW(mannequin.parameters(), lr=1e–2, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e–8, weight_decay=0.1)
# Outline studying charge schedulers warmup_steps = 10 total_steps = 100 min_lr = 1e–4 warmup_lr = LinearLR(optimizer, start_factor=0.1, end_factor=1.0, total_iters=warmup_steps) cosine_lr = CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=total_steps – warmup_steps, eta_min=min_lr) combined_lr = SequentialLR(optimizer, schedulers=[warmup_lr, cosine_lr], milestones=[warmup_steps])
# Coaching loop for step in vary(total_steps): # prepare one epoch y_pred = mannequin(X) loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y) # print loss and studying charge print(f“Step {step+1}/{total_steps}: loss {loss.merchandise():.4f}, lr {combined_lr.get_last_lr()[0]:.4f}”) # backpropagate and replace weights optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() combined_lr.step() |
Operating this code, you may even see:
|
Step 1/100: loss 1.5982, lr 0.0010 Step 2/100: loss 1.5872, lr 0.0019 Step 3/100: loss 1.5665, lr 0.0028 … Step 9/100: loss 1.2738, lr 0.0082 Step 10/100: loss 1.2069, lr 0.0091 Step 11/100: loss 1.1387, lr 0.0100 … Step 98/100: loss 0.4845, lr 0.0001 Step 99/100: loss 0.4845, lr 0.0001 Step 100/100: loss 0.4845, lr 0.0001 |
Discover how the training charge will increase after which decreases.
Sequence Size Scheduling
Language fashions are educated with sequence knowledge. Transformer fashions or recurrent neural networks are each architecturally agnostic to the sequence size. Nonetheless, you might wish to prepare the mannequin with lengthy sequence to let the mannequin learn to deal with lengthy context.
In coaching, lengthy sequence lengths will be problematic. First, you prepare with batches of sequences, and ragged lengths imply you want to pad the sequences to the utmost size within the batch. Whereas you’ll ignore the padded tokens, your mannequin nonetheless must course of them, therefore sources are wasted. Second, within the consideration mechanism, the complexity is quadratic to the sequence size. The longer the sequence, the extra pricey it’s to course of.
Subsequently, you might wish to create batches with sequences of comparable size to keep away from extreme padding.
You may additionally wish to prepare the mannequin with shorter sequences first. You may pace up the coaching course of by shortly forcing the mannequin to study the patterns of the language utilizing shorter sequences. As soon as the mannequin has pretty converged, you may steadily improve the sequence size to assist the mannequin learn to deal with lengthy contexts.
These are widespread strategies in coaching massive language fashions to avoid wasting computational sources. Notice that you just nonetheless arrange the mannequin with a set most sequence size, which impacts the way you configure the positional embeddings. Nonetheless, you don’t exhaust the utmost sequence size till the mannequin has pretty converged.
Implementing sequence size scheduling means you want to write a extra advanced knowledge loader to keep in mind of the present epoch to return the suitable coaching knowledge.
Different Strategies to Assist Coaching Deep Studying Fashions
Random Restart
Coaching a deep studying mannequin is a fancy course of and never straightforward to get proper, particularly for big fashions. One widespread difficulty is the mannequin getting caught in an area minimal and being unable to converge. Utilizing momentum in gradient descent may also help the mannequin escape from native minima, however is just not at all times efficient. One other strategy is to easily restart the coaching should you ever see the mannequin fail to converge.
Random restart is the technique of coaching the mannequin a number of instances from scratch. It makes use of completely different random seeds every time in order that the mannequin begins with completely different preliminary weights and completely different shuffling of the information. That is executed within the hope that you’ll not at all times get caught in the identical native minimal, so you may choose the one with the perfect efficiency. That is best should you can prepare a number of fashions for fewer epochs initially, then choose the perfect mannequin from the pool to complete coaching with extra epochs.
Gradient Clipping
One widespread difficulty in coaching deep studying fashions is gradient explosion. That is particularly widespread should you prepare the mannequin utilizing lower-precision floating-point numbers, through which the vary of the gradient could possibly be too massive to be represented. Gradient clipping is the strategy of limiting the magnitude of the gradient to a secure worth. With out it, you may even see your coaching course of abruptly fail because of the mannequin weights or loss perform changing into NaN or infinity.
There are a number of methods to clip gradients. The most typical one is to clip the gradient such that the L2 norm is lower than a secure worth, akin to 1.0 or 6.0. You may as well clip the gradient to a price vary, akin to -5.0 to five.0.
Gradient clipping by L2 norm means scaling the whole gradient vector if the L2 norm $Vert g_t Vert_2$ is bigger than a secure worth $c$:
$$
hat{g_t} = minbig(1, frac{c}{Vert g_t Vert_2}huge) cdot g_t
$$
However, gradient clipping by worth means setting the gradient to a secure worth each time the gradient exceeds that worth:
$$
hat{g_t} = start{circumstances}
-c & textual content{if } g_t < -c
g_t & textual content{if } -c le g_t le c
c & textual content{if } g_t > c
finish{circumstances}
$$
Utilizing gradient clipping in PyTorch is simple. You should utilize the torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_ perform to clip the gradient by L2 norm, or the torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_value_ perform to clip the gradient by worth. Under is an instance:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim from torch.nn.utils import clip_grad_norm_, clip_grad_value_
# Instance setup mannequin = torch.nn.Linear(10, 1) X, y = torch.randn(5, 10), torch.randn(5) total_steps = 100 loss_fn = nn.MSELoss() optimizer = optim.AdamW(mannequin.parameters(), lr=1e–2, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e–8, weight_decay=0.1)
# Coaching loop for step in vary(total_steps): # prepare one epoch y_pred = mannequin(X) loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y) optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() # clip by L2 norm clip_grad_norm_(mannequin.parameters(), max_norm=1.0) # or clip by worth # clip_grad_value_(mannequin.parameters(), clip_value=1.0) optimizer.step() |
Combined Precision Coaching
When a mannequin turns into too massive, reminiscence consumption turns into a bottleneck as nicely. You could wish to save reminiscence by utilizing lower-precision floating-point numbers in coaching, akin to half precision (float16) or bfloat16. In comparison with single precision (float32), float16 and bfloat16 can scale back reminiscence consumption by half, however the vary and precision are sacrificed.
Subsequently, you might wish to use blended precision coaching, through which a part of the mannequin makes use of float32 whereas the opposite half makes use of float16. A typical selection is to make use of float32 for biases however float16 for weights in linear layers.
Trendy GPUs can run float16 operations on the identical pace as float32, however since you may function on extra knowledge on the identical time, you may successfully run the coaching course of at double pace.
Additional Readings
Under are some sources that you could be discover helpful:
Abstract
On this article, you discovered about some strategies to hurry up the coaching technique of deep studying fashions, particularly for big language fashions. Particularly, you discovered that:
- AdamW with cosine decay is the preferred optimizer and studying charge scheduler for coaching language fashions.
- You should utilize sequence size scheduling to avoid wasting computational sources when coaching language fashions.
- Strategies like random restart and gradient clipping may also help you prepare the mannequin extra stably.
- Combined precision coaching may also help you scale back reminiscence consumption.




