IT groups face mounting challenges as they handle more and more advanced infrastructure and functions, usually spending numerous hours manually figuring out operational points, troubleshooting issues, and performing repetitive upkeep duties. This operational burden diverts invaluable technical sources from innovation and strategic initiatives. Synthetic intelligence for IT operations (AIOps) presents a transformative answer, utilizing AI to automate operational workflows, detect anomalies, and resolve incidents with minimal human intervention. Organizations can optimize their operational effectivity whereas sustaining safety as they handle their infrastructure and functions.
You need to use Amazon Q Developer CLI and Mannequin Context Protocol (MCP) servers to construct highly effective AIOps options that may scale back guide effort by way of pure language interactions. Amazon Q Developer might help builders and IT professionals with a lot of their duties—from coding, testing, and deploying, to troubleshooting, performing safety scanning and fixes, modernizing functions, optimizing AWS sources, and creating knowledge engineering pipelines. The MCP extends these capabilities by enabling Amazon Q to attach with customized instruments and companies by way of a standardized interface, permitting for extra refined operational automations.
On this submit, we talk about how you can implement a low-code no-code AIOps answer that helps organizations monitor, determine, and troubleshoot operational occasions whereas sustaining their safety posture. We present how these applied sciences work collectively to automate repetitive duties, streamline incident response, and improve operational effectivity throughout your group.
That is the third submit in a sequence on AIOps utilizing generative AI companies on AWS. Discuss with the next two posts for constructing AIOps utilizing Amazon Bedrock and Amazon Q Enterprise:
Answer overview
MCP servers act like a common connector for AI fashions, enabling them to work together with exterior methods, fetch reside knowledge, and combine with numerous instruments seamlessly. This helps Amazon Q present extra contextually related help by accessing the knowledge it wants in actual time. The next structure diagram illustrates how you should use a single configuration file, mcp.json, to configure MCP servers in Amazon Q Developer CLI to hook up with exterior methods.
The workflow consists of the next steps:
- The consumer configures an MCP shopper in Amazon Q Developer CLI utilizing the
mcp.jsonfile. - The consumer logs in to Amazon Q Developer CLI and asks operational queries in pure language.
- Relying in your question, Amazon Q decides which MCP servers that you simply configured or current instruments to invoke to carry out the duty.
- The MCP server interacts with the respective exterior system to get the reside knowledge that’s utilized by Amazon Q to carry out the required job.
On this submit, we present how you can use Amazon Q Developer CLI to handle the next operational points:
Conditions
Full the next conditions earlier than you begin organising the demo:
Configure MCP in Amazon Q Developer CLI
MCP configuration in Amazon Q Developer CLI is managed by way of JSON recordsdata. You’ll configure the Amazon Bedrock Information Base Retrieval MCP Server. On the time of writing, solely the stdio transport is supported in Amazon Q Developer CLI.
Amazon Q Developer CLI helps two ranges of MCP configuration:
- World configuration – Makes use of
~/.aws/amazonq/mcp.jsonand applies to all workspaces - Workspace configuration – Makes use of
.amazonq/mcp.jsonand is restricted to the present workspace
For this submit, we use the workspace configuration, however you will have choice to make use of both of them.
- Create a brand new workspace folder, and inside that folder, create the file
.amazonq/mcp.jsonwith the next content material:
See the AWS MCP Servers GitHub repository for an up to date record of accessible MCP servers.
- Open a terminal, navigate to the workspace folder that you simply created, and run the next command to log in to Amazon Q Developer CLI:
- Observe the directions to log in to Amazon Q Developer on the command line.
- Provoke the chat session by working
qafter which run/instrumentsto validate that the Amazon Bedrock Information Base Retrieval MCP server is configured.
Device permissions have two doable states:
- Trusted – Amazon Q can use the instrument with out asking for affirmation every time
- Per-request – Amazon Q should ask in your affirmation every time earlier than utilizing the instrument
By default, this instrument won’t be trusted.
5. Run /instruments belief awslabsbedrock_kb_retrieval_mcp_server___QueryKnowledgeBases to belief the MCP server.
6. Run the /instruments command once more to validate it.
Deploy AWS sources
Deploy the next AWS CloudFormation template to deploy the AWS sources that you’ll use to check AIOps. You’ll be able to deploy this template in both the us-east-1 or us-west-2 AWS Area. You’ll be able to deploy it in different Areas by updating the relevant AMI IDs within the template. This template will deploy two EC2 situations and three S3 buckets.
This CloudFormation template is for demo functions solely and never meant for manufacturing utilization.
Validate that the template deployed two EC2 situations, that are in Operating state.
Moreover, validate that the template created three S3 buckets with the names aiops-qdevcli-bucketX-aiops-qdevcli-
Create an Amazon Bedrock data base
Add the pattern excessive CPU utilization runbook to the aiops-qdevcli-
Use case 1: Determine and remediate excessive CPU utilization in an EC2 occasion
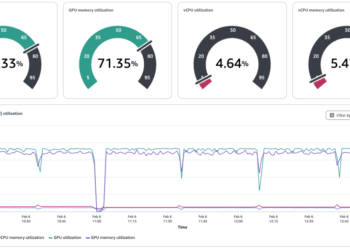
On this use case, you introduce CPU stress in one of many EC2 situations after which use Amazon Q Developer CLI to determine and remediate it.
- On the Amazon EC2 console, log in to the
aiops-qdevcli-high-cpu-utiloccasion utilizing EC2 Occasion Join. - Run the next command to put in
stress-ng:
- Run the next command to emphasize the EC2 occasion for 1 hour:
You could wait roughly 10 minutes for the Amazon CloudWatch alarm to get triggered.
- Return to the Amazon EC2 console and examine that the
aiops-qdevcli-high-cpu-utiloccasion is at the moment in Alarm state. - From the Amazon Q Developer CLI, use a pure language question to examine for operation points in your account. Use the data base ID that you simply saved within the earlier part.
Amazon Q Developer CLI autocorrects the errors that it encountered whereas working the instructions.
Watch the next video for extra particulars.
Because of the inherent nondeterministic nature of the FMs, the responses you obtain from Amazon Q Developer CLI may not be precisely the identical as these proven within the demo.
Use case 2: Determine and take away public entry from an S3 bucket
On this use case, you’ll simulate an unintended safety problem by unblocking public entry for one of many buckets after which use Amazon Q Developer CLI to determine and remediate the difficulty.
- On the Amazon S3 console, open one of many
aiops-qdevcli-xxxxbuckets, and on the Permissions tab, select Edit and alter Block all public entry to Off.
- Return to the Amazon Q Developer CLI and ask questions in pure language to determine and remediate the operational problem.
Watch the next video for extra particulars.
Use case 3: Determine and block a particular undesirable open port for inbound connection to an EC2 occasion
On this use case, you’ll use Amazon Q Developer CLI to determine the EC2 occasion that has a particular port open after which shut the port.
- On the Amazon EC2 console, word that the
aiops-qdevcli-open-port-demooccasion has port 5080 open for all inbound TCP connections. That is an undesirable safety threat that you simply need to determine and remediate.
- Return to Amazon Q Developer CLI and use pure language queries to determine the EC2 occasion with port 5080 open and repair the difficulty.
Watch the next video for particulars.
Clear up
Correctly decommissioning provisioned AWS sources is a crucial greatest observe to optimize prices and improve safety posture after concluding proofs of idea and demonstrations. Full the next steps to delete the sources created in your AWS account:
- On the Amazon Bedrock console, delete the Amazon Bedrock data base.
- On the Amazon S3 console, empty the
aiops-qdevcli-kb-xxxbucket. - On the AWS CloudFormation console, delete the CloudFormation stack.
In its place, attempt the previous steps utilizing pure language queries in Amazon Q Developer CLI.
- Lastly, delete the
.amazonq/mcp.jsonfile out of your workspace folder to take away the MCP configuration for Amazon Q Developer CLI.
Conclusion
On this submit, we confirmed how Amazon Q Developer CLI interprets pure language queries, mechanically converts them into applicable instructions, and identifies the required instruments for execution. The answer’s clever error-handling capabilities analyze logs and carry out auto-corrections, minimizing guide intervention. By implementing Amazon Q Developer CLI, you’ll be able to improve your crew’s operational effectivity, scale back human errors, and handle advanced environments extra successfully by way of a conversational interface.We encourage you to discover extra use instances and share your suggestions with us. For extra data on Amazon Q Developer CLI and AWS MCP servers, check with the next sources:
Concerning the authors
 Biswanath Mukherjee is a Senior Options Architect at Amazon Net Providers. He works with giant strategic clients of AWS by offering them technical steering emigrate and modernize their functions on AWS Cloud. Together with his intensive expertise in cloud structure and migration, he companions with clients to develop revolutionary options that leverage the scalability, reliability, and agility of AWS to fulfill their enterprise wants. His experience spans numerous industries and use instances, enabling clients to unlock the total potential of the AWS Cloud.
Biswanath Mukherjee is a Senior Options Architect at Amazon Net Providers. He works with giant strategic clients of AWS by offering them technical steering emigrate and modernize their functions on AWS Cloud. Together with his intensive expertise in cloud structure and migration, he companions with clients to develop revolutionary options that leverage the scalability, reliability, and agility of AWS to fulfill their enterprise wants. His experience spans numerous industries and use instances, enabling clients to unlock the total potential of the AWS Cloud.
 Upendra V is a Senior Options Architect at Amazon Net Providers, specializing in Generative AI and cloud options. He helps enterprise clients design and deploy production-ready Generative AI workloads, implement Massive Language Fashions (LLMs) and Agentic AI methods, and optimize cloud deployments. With experience in cloud adoption and machine studying, he allows organizations to construct and scale AI-driven functions effectively.
Upendra V is a Senior Options Architect at Amazon Net Providers, specializing in Generative AI and cloud options. He helps enterprise clients design and deploy production-ready Generative AI workloads, implement Massive Language Fashions (LLMs) and Agentic AI methods, and optimize cloud deployments. With experience in cloud adoption and machine studying, he allows organizations to construct and scale AI-driven functions effectively.